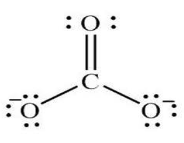
Carbonate Ion Formula
Carbonate ion, possibly a chemical compound or salt of acid in a carbon oxyanion. Bicarbonate is the compound acid of carbonate. It is a sophomore form and a polyatomic ion. However, it plays a vital role in the science of buffering pH systems.
The Formula for Carbonate Ion
It may be an anion and reckons a trigonal coplanar unit structure. It belongs to an atom bordered by three oxygen atoms. In addition, it may be a reasonably powerful base.
So by the explanation of Lewis base attracts protons in the aqua solution.
Chemical Formula = CO32-
Properties of Carbonate
A few major properties of carbonate ions are mentioned below:
Physical State
- Carbonates are in their solid state at room temperature.
- The carbonates of group 2 are more covalent than compared to the carbonate of group 1
- The carbonates of group 2 and group 1 are colourless, but on the other hand, the carbonates of transition elements are coloured in nature.
Solubility
- Carbonates of group 1 a solvable in water
- Carbonates of group 2 are meagerly soluble in water
- Carbonates of group 2 are moderately soluble in the chemical solution CO2.
Thermal Stability
- On being heated, the carbonate dissociates into carbon dioxide and oxide.
- The thermal stability of group 2 and group 1 of carbonates increases when we go down the group.
Uses of Carbonate
- It is used to warm water or soften water
- Used in the manufacturing of glass
- Used as a natural material for the manufacture of papers
- Carbonate ions such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate are utilized in washing detergents.
Solved Problems
1. How are carbonate and water formed from its ions?
Hydrogen carbonates are amphiprotic because they play as both anaemic acids and anaemic bases. Consequently, it plays as acids and responds with solutions of soluble hydroxides to create carbonate and water.
Reaction:
KHCO3(aq) + KOH(aq) → K2CO3(aq) + H2O(aq)
2. How do carbonate ions act as a base?
Carbonate ions are compounds with ions of hydrogen in two stages. The first-hand step is to build bicarbonate ions, and hence, the next step is to render water and CO2.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out