Bond Order Formula
The number of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule is known as bond order.
The number of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule is known as bond order.
The shorter the bond length and the stronger the bond, the more bonds there are between two atoms. As a result, triple bonds are shorter than double bonds, which are shorter than single bonds.
The value “zero” of the bond order indicates that there is no bond present between the atoms.
The increase in the value of bond order indicates the strengthening of the bond
The formula for the calculation of the bond order is
Bond Order = (Number of bonding electrons – Number of antibonding electrons) / 2
Get answers to the most common queries related to the Bond Order Formula.
Answer: The more the bond order, the smaller the bond length. They both are inversely related.
Answer: The more the bond order, the smaller the bond length. They both are inversely related.
Answer:
Molecular orbital diagram of nitrogen molecule:
Given molecule – Nitrogen
Element – Nitrogen
Atomic number of nitrogen – 7
Electronic configuration – 1s²2s²2p³
Total number of electrons in nitrogen molecule – 14
Molecular orbital diagram of N2 is as follows;
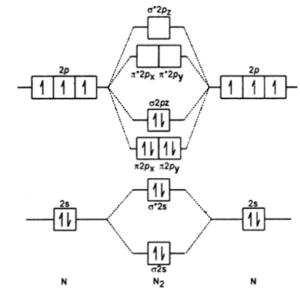
Electronic configuration: 1s² < *1s² < 2s² < *2s² , [ 2px² = 2py²] < 2pz² < [*2px =*2py] < *2pz
Let’s calculate the bond order of N2;
Bond order = Bonding electrons – Anti bonding electrons / 2
= 10 – 4 / 2 = 3
Therefore, the order of N2 is 3.
Answer: The bond length is proportional to the atom’s size, and the bond dissociation energy, or bond strength, is proportional to the atom’s size.
The bond dissociation energy of a bond increases as the bond multiplicity increases.
The repulsion between linked atoms grows as the number of lone pairs of electrons increases, and the bond dissociation energy decreases.
Note:
Bond strength is the strength with which a chemical bond keeps two atoms together. This is commonly described in terms of how much energy is necessary to break the connection in the first place. Its unit is kilocalories per mole.
The energy required to produce free radicals from the atoms that formed that particular bond was provided by bond dissociation energy.