The administration of the whole country cannot just go by only one rule; that is why for the proper functioning of the country the powers and the responsibilities are equally divided into smaller internal parts into states, Union Territories, and different smaller districts. The detailed discussion has been given below.
Union territories
The union territories are a type of administrative division in the country, India. The union territories are unlike the states in the country, their territories are federally governed by the union of the government of India whereas the states of the country have their own government to run the state.
After the independence of the country of India in the year 1949, the Indian Constitution was adopted by the government for the better functioning of the country and the welfare of the citizens of the country.
In the constitution, part C concluded that the princely states will be governed by the chief commissioners who were appointed by the President of India. The princely states included Ajmer, Bhopal, Court Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Tripura, Manipur, catch, and Vindhya Pradesh. Similarly, part D of the constitution said that the Andaman and the Nicobar Islands must be administered by the Lieutenant Governor who is appointed by the Center.
Ever after, the act of State’s Recognition was implied in the year 1956 the part D and the Part C of the Indian Constitution were joined to form the set of union territories that included:
- The Andaman and the Nicobar Islands
- Lakshadweep
- Manipur
- Himachal Pradesh and
- Tripura
- Delhi
In November of the year 2019, there were new changes made in the Indian Constitution, which added more union territories to the list.
The current union territories are:
- Puducherry
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Delhi
- Chandigarh
- Andaman and the Nicobar Islands
- Daman and Diu together with the Dadra and the Nagar Haveli
States of India
By the Union Federation of India, there are now 28 states in total with 36 different entities. Also, the states of the country have been divided into smaller administrations and different smaller districts. In simpler terms, the states are the smaller internal division in any country.
The former governors’ who were also in the times of British India were given to rule the regions mentioned in part A of the Constitution of India. These areas were:
- The west Bengal
- Madras
- Eastern Punjab
- Bombay
- Bihar
- Assam
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh and
- Orissa
Part B of the constitution included the regions which were ruled by the Rajpramukhs; the President of the country used to appoint the Rajpramukh of any particular region they wanted to.
The new 28 states of the country are as follows:
- Kerala
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Odisha
- Assam
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Chhattisgarh
- Jharkhand
- Maharashtra
- Maharashtra Pradesh
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Nagaland
- Mizoram
- Punjab
- Sikkim
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Rajasthan
- West Bengal
- Tripura
- Telangana
- Tamil Nadu
- Bihar
- Himachal Pradesh
Every state has its government, and the representation of the leaders of the states is purely dependent on the regular elections which are held every five years.
Difference between Union Territory and the States of India
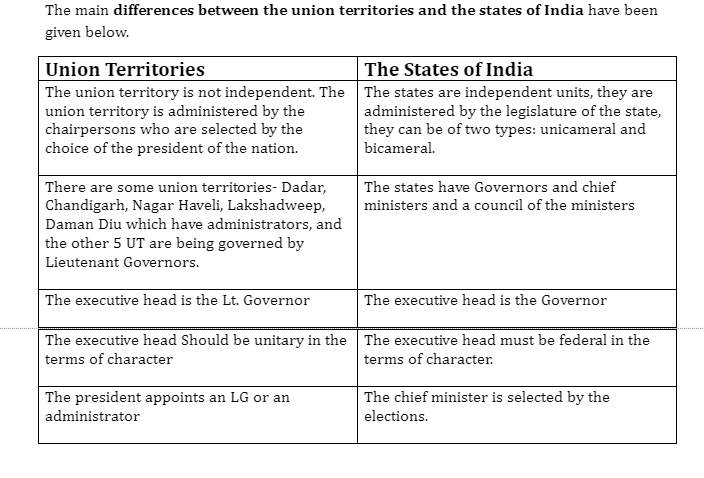
Conclusion
As has been mentioned above, the union territories are a type of administrative division in the country, India. The union territories are unlike the states in the country, their territories are federally governed by the union of the government of India whereas the states of the country have their own government to run the state. Some new changes were done in the year 2019, that was Ladakh, and the state of Jammu and Kashmir was put in the category of Union Territories. Also, the key difference between a union territory and a state has been mentioned.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



