What Are the Valencies of Sulphur in SO2 and SO2?
We must be aware that sulphur is an element found in period 3 of the contemporary periodic table. Sulphur can have an extended valency is the key to understanding its significance. Its valency can range anywhere from -1 to +6, inclusive. As a result, the highest possible valency for sulfur is 6. Because of this, broad valency can easily form bonds with ions of numerous types of atoms, including cations and anions.
We must keep in mind that the outermost shell of the sulphur atom contains six electrons. However, it can also have a valency of 2 and a value of 6.
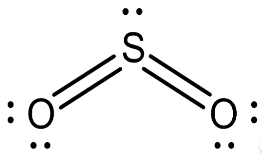
First, let’s take a look at some SO2 molecules. One atom of sulphur and two oxygen atoms have formed a connection in this instance.
We are aware that the valency of oxygen atoms is equal to 2. It contains six atoms in the outermost shell, and for it to complete its octet, it requires just two electrons from another atom that is bonding with it. We need a total of four electrons to create two atoms of oxygen.
Therefore, in this particular instance, the valency of sulfur in the SO2 molecule is +4.
At this point, we can depict the structure of SO2 as,
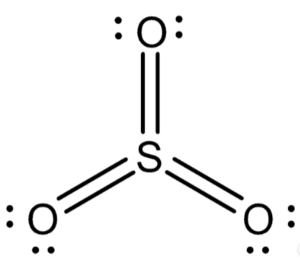
Now, sulfur trioxide has a structure that consists of three oxygen atoms bound to a single sulfur atom.
The combined valency of three atoms of oxygen is negative six. Because of this, the valency of sulphur in sulphur trioxide is +6, which is sufficient to compensate for the -6 valency of the three oxygen atoms.
At this point, we can depict the structure of SO3 as,
 We must remember that some elements, such as sulphur and phosphorus, have extended valencies. This is since their valence shell has enough orbitals to accept more electrons. Sulphur, for example, contains empty d-orbitals to receive electrons. That is why sulphur dioxide has a +4 valency, whereas sulphur trioxide has a +6 valency.
We must remember that some elements, such as sulphur and phosphorus, have extended valencies. This is since their valence shell has enough orbitals to accept more electrons. Sulphur, for example, contains empty d-orbitals to receive electrons. That is why sulphur dioxide has a +4 valency, whereas sulphur trioxide has a +6 valency.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out