Draw the Electron Dot Structures for (a) ethanoic acid (b) H2S (c) propanone (d) F2
Many different terms are used for Lewis structures, including electron dot structures and Lewis dot diagrams. In all cases, the same types of diagrams are used to indicate where electrons and bonds are located. Lewis structures are diagrams that indicate where covalent bonds and electron pairs occur in molecules. An octet rule governs Lewis structures. Lewis structures are useful for understanding chemical bonding. However, they lack the ability to account for aromaticity and do not accurately mimic magnetic behaviour.
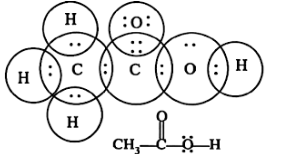
(a) Ethanoic Acid
The acidic portion of ethanoic acid is a monocarboxylic acid containing two carbons. Besides regulating the acidity of food, it is also used as an antimicrobial food preservative and a Daphnia magna metabolite. It is an acetate conjugate acid.
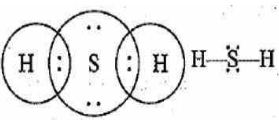
(b) H2S
The Lewis structures of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) contain two single bonds surrounding sulphur atoms. The sulphur atoms also have two lone pairs. The Lewis structure of H2S is based on the number of total valence electrons present in sulphur and hydrogen atoms.
(c) Propanone
The simplest and smallest ketone, propanone, is chemically defined as (CH3)2CO, and it is the most common substance called “acetone.”.
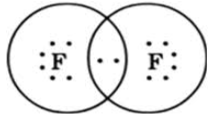
(d) F2
An electron is represented by a dot. One electron is needed to complete a fluorine octet. When fluorine atoms combine, each fluorine shares 1 electron, forming a single bond between them.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out