Draw a Neat Labelled Diagram of the Plant Cell
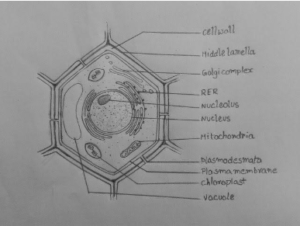
Structure of a Plant Cell
- Cell wall
- Middle Lamella
- Plasma membrane
- Golgi complex
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Mitochondria
- Plasmodesmata
- Chloroplast
- Vacuole
Cell wall: A cell wall is an outer covering of cells in plants and algae that can be a physical barrier or may provide support. A cell wall forms the primary boundary of the cell, separating the cytoplasm from the external environment.
Middle Lamella: Middle lamella is a single layer of endodermal cells, which form a layer between the outer primary cell wall and the inner secondary cell wall.
Plasma membrane: The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer that forms the surface of a cell and regulates what moves in and out.
Plant Golgi body (or Golgi apparatus): The Golgi body is a stack of flattened membranous sacs where macromolecules are processed. Cholesterol and steroid hormones are produced by the plant cell.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (or rough ER): Rough ER is formed in the cytosol of cells and is sometimes called rough ER because it lacks puncta, which are holes in the cell membrane where proteins can move from one end of the cell to another.
Nucleus: The nucleus is composed of DNA and ribosomes that translate the DNA into proteins. Cis-acting elements are located in the plant nucleus, such as those involved in the control of cell growth.
Nucleolus: The nucleolus is the site of ribosomes and synthesizes rRNA. The nucleolus forms in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are sites of respiration by oxidative phosphorylation.
Plasmodesmata: Plasmodesmata are channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells, enabling the transport of proteins, vesicles, RNA, small molecules and ions.
Chloroplast: The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis and is located in the cytoplasm of a plant cell. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are performed by chloroplasts in plants.
Vacuole: A vacuole is a structure that stores water and other solutes and provides storage for damaged organelles.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






