The biochemical cycle in an ecosystem is defined as the transformation and transport of chemicals in ecosystems. In wetlands, by unique hydrological conditions, biogeochemical cycles are strongly influenced. Within wetlands, these processes result in changes in the movement of materials and also in the chemical form of materials. The overall wetland productivity is determined by this process.
The biogeochemical cycle includes several chemical elements, the main chemical elements like oxygen, water, carbon, nitrogen, calcium selenium, sulfur, etc. in which between the biotic and abiotic factors movements of nutrients and other elements occur. Essential elements of living matter are circulated by a natural cycle called the biogeochemical cycle. The geological, biological, and chemical aspects of each cycle are together considered as a biogeochemical cycle. With the acronym CHNOPS, the fundamental elements of the biogeochemical cycle like Carbon(C), Hydrogen(H), Nitrogen(N), Oxygen(O), Phosphorous(P), and Sulphur(S) can be easily remembered. These elements get circulated through the biotic and abiotic components; biotic refers to the living components and abiotic refers to the nonliving components. There can be three types of abiotic components like the lithosphere i.e the rick, the hydrosphere i.e. the water, and the atmosphere i.e. the air. The biogeochemical cycle in simple form can be explained as nothing but the chemical exchange between living organisms i.e. from where the term ‘bio’ comes from and the geographic element of the earth such as rock, soil, water, and air.
Important Biogeochemical cycle in the ecosystem
There are four main important biogeochemical cycles in the ecosystem are as follows –
- Oxygen Cycle
- Water Cycle or Hydrologic cycle
- Carbon Cycle
- Nitrogen Cycle
Oxygen Cycle
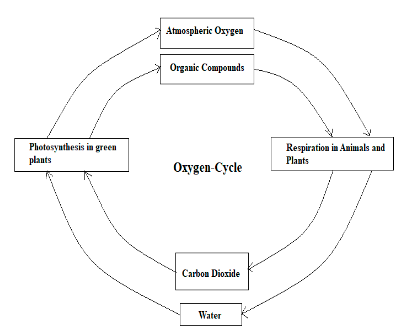
Within the biosphere, the circulation and recycling of oxygen are called the oxygen cycle. Oxygen is found in various forms in the atmosphere like water (H2O), molecular oxygen (O2), inorganic compounds, carbon dioxide (CO2), etc. 21% percent of the atmosphere is made up of oxygen, it is also present in lithosphere and hydrosphere, both biotic and abiotic components are included in this cycle. Oxygen is continuously produced as well as used up in the atmosphere, oxygen is a highly reactive element and it readily reacts with other compounds and elements. The oxygen cycle in the biosphere is extremely complex. Oxygen is released from plants by photosynthesis whereas it is used up in the processes like combustion, rusting, corrosion, respiration, decomposition, etc. Most of the microorganisms use oxygen for respiration, such microorganisms are known as aerobes and the microorganisms that do not need oxygen are called anaerobes. For the synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, fats oxygen is required; oxygen is also used in various chemical reactions. Through various atmospheric processes ozone (O3) is produced from oxygen.
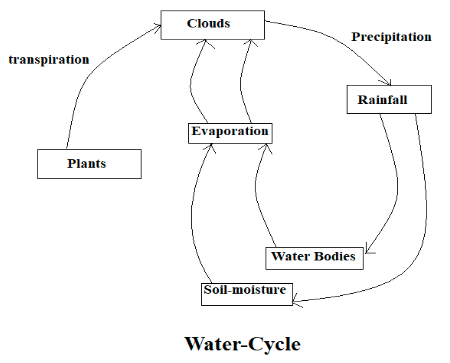
Water Cycle
Due to the heat of the sun water evaporates from lakes, seas, rivers, and other water bodies; this process is known as evaporation, water also evaporates from the plant’s leaves, which is known as transpiration. As the water rises from lakes, seas, rivers, and other water bodies in the atmosphere, it gets cool and condenses to form clouds as a continuous process of evaporation and condensation, gradually the clouds get heavy, and as a result, precipitation occurs in the form of rain. And this rainwater is stored in any of the following reservoirs such as the ocean, soils, glaciers, under the Earth’s surface as groundwater, lakes, snowfields, etc.
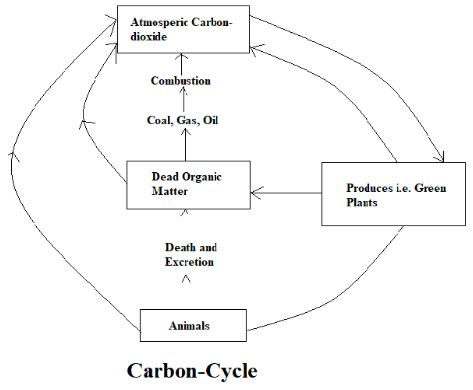
Carbon-Cycle
The carbon concentration in the atmosphere is about 0.03%. Circulation of carbon from the atmosphere to the biosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and returns to the atmosphere is known as the carbon cycle. The carbon from the atmosphere enters into the plants through photosynthesis for synthesizing food particles, when the plants are consumed by terrestrial organisms, carbon dioxide enters them. When these terrestrial organisms die the carbon dioxide enters the soil. Carbon dioxide enters into the water as carbonates, which helps the aquatic plants to perform photosynthesis. CO2 returns to the atmosphere from fossil fuel, from respiration of animals, the release of smoke from vehicles, from the burning of wood. If CO2 increases in the atmosphere it disturbs the natural carbon cycle.
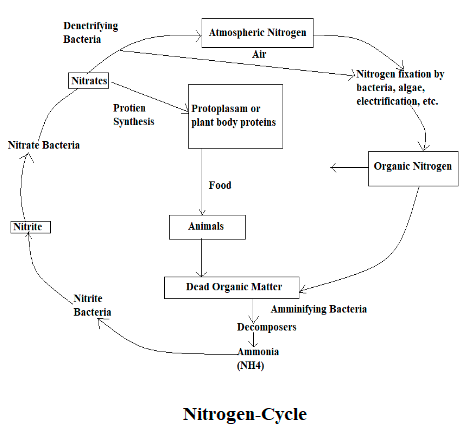
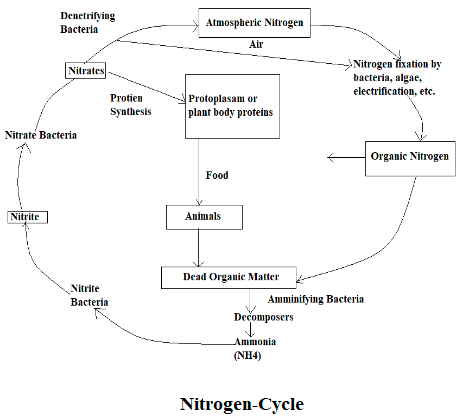
Nitrogen Cycle
The atmosphere is made up of 78% Nitrogen; we need nitrogen for DNA and proteins. Nitrogen that is available in the atmosphere cannot be directly consumed by plants, they can consume the nitrogen when it is fixed i.e. when combined with other elements like carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. By the action of denitrifying bacteria, nitrogen is spontaneously entering into the air and through the action of electrification and lightning, nitrogen is entering into the soil.
Conclusion
It is to conclude that the biochemical cycle in an ecosystem is defined as the transformation and transport of chemicals in ecosystems. In wetlands, by unique hydrological conditions, biogeochemical cycles are strongly influenced. There are four main important biogeochemical cycles in the ecosystem are oxygen cycle, water cycle or hydrologic, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out