India won its Independence and defeated British rule in 1947. The British Dictatorship was prevalent from 1858 to 1947. A constituent assembly was set up to draft the constitution for free India. This constituent assembly was a sovereign body made up of many committees.
Different committees of the constituent assembly worked together to draft the constitution and the Indian political body as we know it.
What is the Constituent Assembly of India?
Known as the first Parliament of an Independent India, The Constituent Assembly was a sovereign body formed to help in the constitution-making process for the newly independent India. The Cabinet Mission Plan was in charge of creating the Constituent Assembly of the country.
The Cabinet Mission Plan scrapped the universal adult franchise voting system that we have right now. But it rather suggested that the members of the different committees of the constituent assembly be elected by the provincial assemblies that were also only recently elected.
As a result, members of the provincial assembly cast their single, transferable vote to elect the members of the different committees of the constituent assembly.
The number of members elected by the Provincial Assembly was 292. There were more contributions made by the Princely States and the Chief Commissioner provinces of Coorg, Delhi, Ajmer-Merwara and British Baluchistan. The Princely States added 93 members, while the Chief Commissioner provinces added 4 members.
The seats to the Princely States and The Provinces were allotted based on their respective population. It was to be divided among Sikhs, Muslims and all other communities so that every section had a representative in the Constituent Assembly.
Before the partition of India and Pakistan, the strength of the Constituent Assembly was 389 members. But after partition, the number of seats came down to 299 since some princely states and some provinces had become part of the newly formed Pakistan.
The Constituent Assembly held the first meeting of the newly formed parliament on December 9, 1946, and Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha was appointed as the interim president of the Constituent Assembly. Ultimately, Dr Rajendra Prasad was elected as the president of the constituent assembly on December 11, 1946, and the vice president was Harendra Coomar Mookerjee.
What are the Committees of the Constituent Assembly?
Different Committees were set up by the constituent assembly to look towards the different departments of Constitution-making, for now, an Independent India.
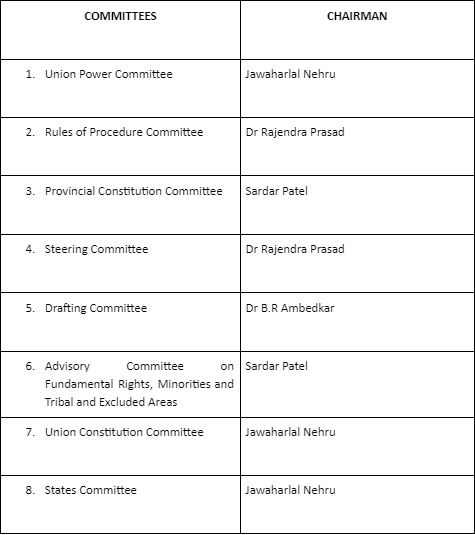
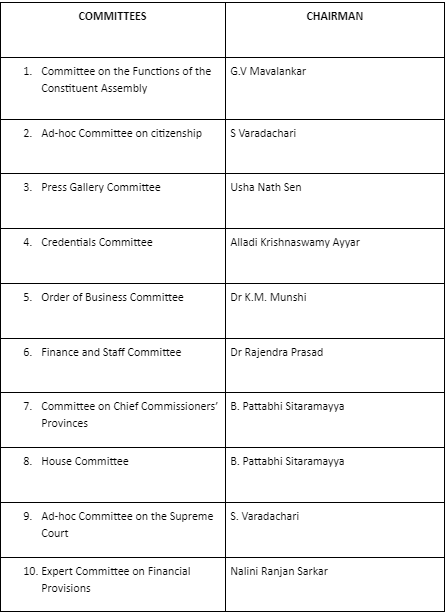
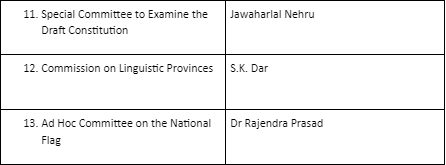
There were a total of 22 committees of the constituent assembly. Among them, only 8 were the most important committees, while the remaining were the minor and supporting committees.
10 committees handled Procedural affairs. 12 committees handled substantive affairs.
Given its critical responsibility of drafting a constitution, the Drafting Committee is undoubtedly very prominent in the history of Indian Polity.
Drafting Committee
The drafting committee was one of the eight most important committees of the Constituent Assembly. It was set up on 29th August 1947, by the constituent assembly. At the first meeting of the Drafting Committee on 30th August 1947, the chairman of the committee was elected as Dr B.R Ambedkar.
It was the most important committee as it was entrusted with the responsibility of drafting a new constitution for India based on the reports submitted by the other committees of the constituent assembly.
The drafting committee published the first draft of the would-be constitution on 21st February 1948. It was then scrutinised by the citizens of India for about eight months. Further amendments were also proposed by the citizens.
After hearing the feedback from the public, the necessary amendments were made and the following draft of the constitution was published in October 1948.
Since its inception in 1947, the drafting committee took 2 years, 11 months and 17 days to frame the full Constitution of India.
The constituent Assembly had held a total of 11 sessions over the course of 165 days. Out of these, 114 days were spent on the deliberations of the drafting committee and the draft(s) Constitution.
A total of seven members made up the prominent Drafting Committee. These members are:
- B.R. Ambedkar – Chairman
- Alladi Krishnaswami Ayyar
- K.M Munshi
- B.L. Mitter
- D.P. Khaitan
- Mohammad Saadulla
- N. Gopalaswami
Important Committees of the Constituent Assembly and their Chairman
Major Committees of the Constituent Assembly are:
Minor Committees of the Constituent Assembly
Conclusion
The constitution was formed after the joint effort of the 22 committees of the constituent assembly. After various amendments and almost 3 years, the final draft of the constitution was submitted on November 4th, 1948.
November 26, 1949, marked as the day when the Indian Constitution was finally approved. . On January 26, 1950, the constitution was formally adopted. This is also known as Republic Day.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out







