Newton’s Law of Gravitation tells us that the gravitational force (F), between two quantities or points of masses M and m, are separated by some distance r. This field acts along the line joining their centres, and is proportional to the masses. The gravitational field is also inversely proportional to the square of their distance.
You can write this as
F ∝ Mm / r²
Here, the SI unit of the constant of proportionality can be written as G, whereas the constant gravitational value will be taken as 6.67 x 10-11 Nm 2 kg -2
Thus, you can write the law of gravitational field as
F =GMm/ r²
The gravitational field can be defined as the gravitational force per unit mass that a tiny mass would exert at some point. It is a vector field that points in the direction of the force exerted by the mass. If the point of a particle of mass M is the magnitude of the resultant gravitational field strength at a given distance r from M.
The mathematical equation thus becomes:
g = GM /r²
The gravitational force which will act on the mass can be described with its weight as
F = mg
On the surface of the Earth, g has the magnitude of GM / R²E = 9.81 m s-, here, RE is the radius of the Earth.
The gravitational field can be said as the gravitational force felt by a tiny unit mass placed at any point P in space. Visualise the gravitational field; you can picture a vector that represents the gravitational force on a one-kilogram object at various points in space. You can also watch how the pattern of these vectors varies from one place to another (but in a small room, they won’t vary much!)
You can assume that it’s “a little unit mass” because we don’t want the test mass’s gravitational field that can disrupt the system.
We’ll look at a series of progressively more interesting systems to get an idea of what various gravitational fields look like, starting with a simple point mass and working our way up to a hollow spherical shell. We also need to understand the Earth’s gravitational field, both outside and inside the Earth.
Field from a Single Point Mass
This is the simplest equation. We already know that the gravitational field has the strength of GM/ r², which points towards the mass — which is towards the direction of attraction.
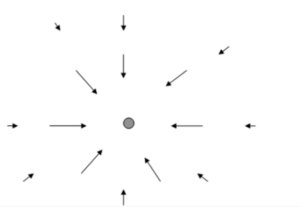
In this figure, you can see this is an inaccurate representation with lots of blank spaces and a field that attracts in different directions. Some vectors point to the mass in the air. But, you cannot get the general idea from the picture.
A different method to portray a field is used to draw “field lines,” which are curves that have the same direction as the field at each point along their length. The field lines provide you with little insight into a single mass.
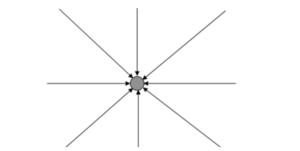
In this diagram, the arrowheads indicate the force’s direction, and it is the same along the field line. The field lines have a flaw in that. From the image, you can see the general impression of the field. It does not provide an exact estimate of the field’s strength at any point of the masses. However, in the image, we can see: the force is greater than the lines that are closer together. A spoke-like field line might be placed anywhere, but if you want to show the field strength, you will need additional lines evenly spaced around the mass and in three dimensions.
Gravitational Field for Two Masses
In the next example, we will talk about two equal masses. If we place them symmetrically from above and below to the x-axis
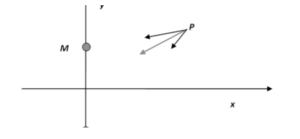
If you recall Newton’s law of gravitational field that has any two masses with mutual gravitational attraction Gm1 m2/r². Then at any point of mass m= 1 at P will feel attraction towards both masses M. It also has a total gravitational field that will be equal to the vector sum of these two sums. These forces are shown with a red line in the diagram.
Question: When the upward force of air resistance is equal to one-fourth of their weight, what is the acceleration of two falling skydivers (total mass = 143kg including parachute)?
Explanation: two forces will act on the skydivers. The first force will be gravity ( i.e. their weight ), which can be represented by Fg. The second force would be the resistance force that will push them against gravity, which can be written as Fai.
The net force exerted on these two objects, as per Newton’s 2nd law, is equal to their mass times their acceleration.
Fnet = ma
The total net force will be the sum of two forces acting simultaneously.
Fnet = Fg + Fair
We know that air resistance is equal to 25% of their total weight and acts in the opposite direction of gravity.
Fair = -¼Fg
You can now substitute the values into this net force equation.
Fnet = Fg – ¼Fg
Now simplifying this,
Fnet= ¾ Fg = ma
Then, the force of gravity can be determined by multiplying the mass by acceleration caused due to gravity.
Fg = mg
Fg = (143 ) ( 9.8 m/ s²)
Fg = 1401.4 N
Substituting these values in the equation.
¾ (1401.4 N) = (143 kg ) a
A = 7.35 m/ s²
Conclusion
A gravitational field is a physics model that describes the effects that a huge body has on the space around it, exerting a force on another heavy body. A gravitational field, which is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg), is used to describe gravitational processes.
The net force exerted on these two objects, as per Newton’s 2nd law, is equal to their mass times their acceleration.
Fnet = ma
The total net force will be the sum of two forces acting simultaneously.
Fnet = Fg + Fair
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






