The fundamental purpose of a resistor is to control the passage of current. Resistors are used for a variety of purposes, including heating, splitting voltages, and numerous circuit operations. In this post, we’ll learn more about resistors, including their applications and uses, as well as the formula for calculating resistance.
Resistor
A resistor is a two-terminal passive electrical component which acts as a circuit element by implementing electrical resistance. Resistors are employed in electronic circuits for a variety of purposes, including reducing current flow, modifying signal levels, dividing voltages, biassing active devices, and terminating transmission lines. High-power resistors can be employed in motor controllers, power distribution systems, or as generator test loads because they can dissipate several watts of electrical power as heat.
The resistance of fixed resistors varies only significantly with temperature, time, or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to alter circuit elements (including a volume control or a lamp dimmer) or as heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity sensing devices.
The resistance of a resistor determines its electrical function; standard commercial resistors come in a range of more than nine orders of magnitude. The resistance’s nominal value is within the manufacturing margin specified on the component.
Need of resistor
We require materials with a specified resistance to accomplish specific functions. Resistors assist us in measuring various resistances and controlling the flow of various electrons.
It’s made up of several colour codes that correspond to specific resistance values which we need for various circuits. These are mostly used to control the amount of resistance that passes through various electrical circuits.
Applications and Uses of resistors
Resistors are useful in the following situations:
Oscillators.
Telecommunications
Amplifiers
Digital Multimeters
Modulators
De-modulators
Transmitters
Now let us look at how resistors are used in various appliances:
Use of resistors in Circuit Functions
A resistor knob is used to control the flow of resistance in the majority of circuits. Resistors are employed in huge machinery to prevent the appliance from being damaged.
Main uses of this knob type resistor:
Controlling the amplifier signal’s volume.
Controlling the motor and other machinery’s speed.
Resistors in LED and Transistors
LEDs are renowned for their low electricity usage due to their inability to conduct a large quantity of current. As a result, resistors are placed between the semiconductors to improve control.
Resistors for heating purposes
As we all understand, collisions between electrons and ions generate heat, which is used in a variety of domestic appliances such as heaters and toasters. These resistors are also used in electric cookers, microwaves, and cleaning equipment. Whenever electricity is transmitted through a bulb’s metal filament, it shines white-hot due to the high temperature generated by the resistance.
Resistors in Dividing Voltages
Since each component requires a separate voltage, splitting voltages can contribute to the smooth operation of the components. By connecting the resistors in series, the voltage will be reduced evenly along each resistor.
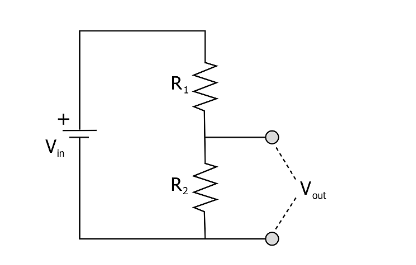
Resistors in Amplifiers
The amplifier is used to enhance the volume of the music. It primarily uses resistors to generate various signals and clock pulses for varied resistances.
Resistors as Temperature Sensors
Some resistors alter resistance as a function of temperature. These can be used as temperature sensors, and they’re connected to systems which can automatically lower the Air Conditioner’s temperature based on the room temperature.
Resistors in bulbs
The heat created by the collision of electrons and ions in the resistor generates white light in the bulb. For the creation of light, most filament bulbs have a resistor in them.
Blinking lights and rainbow lights
The blinking lights must blink at a specific time, as well as the resistor determines how much current we must transmit for the blinking. Color-coding resistors will also change the frequency of flow in the rainbow lights.
How to choose a Braking resistor?
Braking resistors are used in a motor control system to minimise hardware damage and/or nuisance failures in a variable frequency drive (VFD). They’re necessary because, in some situations, the VFD-controlled motor acts as a generator, with power flowing back to the VFD rather than to the motor.
When choosing a braking resistor, the resistance value and the resistor’s power dissipation capacity are the two most important considerations.
Minimum Resistance Value
A “chopper circuit” or brake transistor is included in VFDs which use a brake resistor. The brake transistor shunts current from the DC bus across the braking resistor whenever the DC bus voltage rises too high. Current barriers exist in this brake transistor circuitry, and the VFD manufacturer will normally indicate a maximum current value and duty cycle.
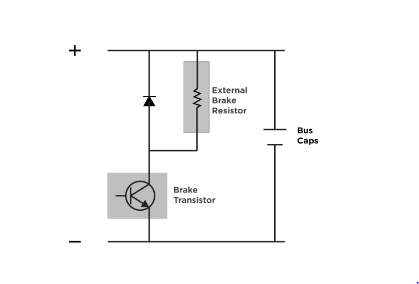
Power Dissipation Capacity
The capacity to dissipate power is the second factor to consider when choosing a brake resistor. The amount of power that KEB brake resistors can safely dissipate if operated constantly (PD) is stated, as well as three values for intermittent duty.
Photoresistor Uses
The most common light sensors are photoresistors. They are frequently used to detect the presence and absence of light or to quantify the intensity of light. Night lights and photographic light metres are two instances.
Things to Remember
The fundamental purpose of a resistor is to control the passage of current.
Resistors assist us in measuring various resistances and controlling the flow of various electrons.
Whenever electricity is transmitted through a bulb’s metal filament, it shines white-hot due to the high temperature generated by the resistance.
For varied resistances, resistors are primarily employed in amplifiers to generate various signals and clock pulses.
Because each component requires a separate voltage, employing resistors to divide voltages can assist in the smooth operation of the components.
Conclusion
A resistor is a two-terminal passive electric device that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. Resistors are used in electronic circuits to reduce current flow, change signal levels, divide voltages, bias active devices, and terminate transmission lines, among other things. To perform various functions, we need materials with a given resistance. Resistors help us measure different resistances and control the passage of different electrons.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



