We know that there is breaking and forming bonds between different compounds in organic chemistry. These bonds are formed by reactions like addition, elimination, substitution, oxidation-reduction, etc. Let us talk about a reaction that replaces the functional group or atom of a compound with the other reacting compound, which is the substitution reaction. The name itself tells us about its working. We also get to know here the meaning and types of substitution and the components that take part during the reaction.
The type of organic reaction in which the functional group replaces the atom or other functional group attached to that atom during a compound is called substitution reaction.
Components of a Substitution Reaction
- Electrophile: It is the species that accepts the electron.
- Nucleophile: It is the species that donates the electron.
- Product: The final species formed as the result of the reaction.
- Leaving group: A group that leaves the compound.
Three types of substitutions reactions
Nucleophilic substitution
In an organic (and inorganic) chemistry, nucleophilic substitution may be a fundamental class of reactions during which a nucleophile selectively bonds with or attacks the positive or partial charge on an atom or a group of atoms. During this process, the weaker nucleophile is replaced by the stronger nucleophile; thus, we can say the weaker nucleophile becomes the leaving group. Another positive and partially positive atom that stays is under the category of an electrophile.
Some samples of nucleophiles are Cl–, OH–, Br–, I–, CN–, H2O, RO–, and NH3.
Nucleophile reaction types
- SN1 substitution reaction
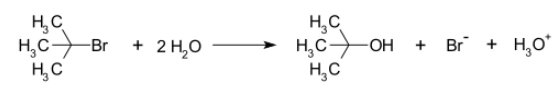
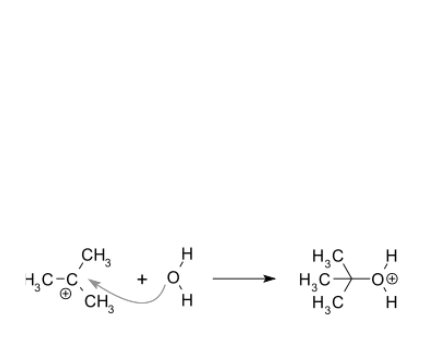
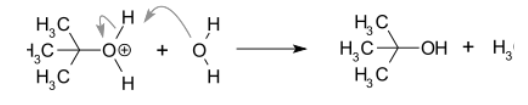
SN1 reaction occurs in conditions when the amount of intermediate is much less than the amount of nucleophile. In the SN1 reaction, “SN” stands for “nucleophilic substitution”, and therefore the “1” denotes that the rate-determining step is unimolecular. Thus, the rate of the equation is usually shown as having first-order dependence on electrophile and zero-order dependence on nucleophile.
An example of a reaction taking place with an SN1 mechanism is the hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide forming tert-butanol.
- SN2 substitution reaction
This is the mechanism where the bond breaking and bond formation takes place simultaneously, i.e., synchronously, or we can say in one step. Since two reacting species are involved within the slow (rate-determining) step, this results in the term substitution nucleophilic (bi-molecular) or SN2. In an example of the SN2 reaction, Br− (the nucleophile) attack on a local anaesthetic (the electrophile) leads to ethyl bromide, with chloride ejected because of the leaving group.
- Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
The displacement of an honest leaving group like a halide from the aromatic ring by the nucleophile is called the aromatic nucleophile substitution. Mechanisms of nucleophilic aromatic substitution are:
- The SNAr (addition-elimination) mechanism
- The aromatic SN1 mechanism encountered with diazonium salts
- The benzyne mechanism (E1cb-AdN)
- The free radical SRN1 mechanism
- ANRORC mechanism
- Vicarious nucleophilic substitution
Electrophilic substitution
When the substituent is electron-deficient (electrophile) and accepts an electron pair for bonding with the compound, which will change, it’s called an electrophilic substitution. Examples related to electrophiles are H3O+, NO2+, and SO3.
Types of electrophilic substitution
- Electrophilic aliphatic substitution
In this electrophilic substitution type, an atom attached to the aromatic ring, mostly hydrogen, is substituted by an electrophile. The reactions that happen are known as aromatic halogenation, aromatic acylation and sulfonation, and aromatic nitration. Also, they are composed of alkylation and acylation.
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution
In this reaction, an electrophile dislocates one among the functional groups. The four electrophilic aliphatic substitution reactions that are similar to counterparts of nucleophile SN1 and SN2 are given as – SE1, SE2, SE2 and SEi (which are called Substitution Electrophilic). During the SE1 reaction, the substrate ionises to the carbanion and recombines with the electrophile. In the SE2 reaction, there is one state of transition in which the old and newly formed bonds are present.
Radical substitution
Radical substitution occurs when an atom or group of atoms during a molecule is replaced by a radical. Some samples of free radicals are Br, Cl, I, and OH.
Applications of radical substitution
- Barton-McCombie deoxygenation
- Dowd-Beckwith reaction
- Wohl-Ziegler reaction
- Minisci reaction
- Hunsdiecker reaction
- Barton reaction
Conclusion
From the above, we can conclude that this reaction is the type that occurs when one functional group or atom replaces the other functional group or atom. The neutrophile electrophile plays a major part in the working of the reaction. In the end, the product and the leaving group are formed. Thus, we can say that this reaction will be useful if we want to extract an element bond with a compound. Also, different types of substitution reactions can be carried out by regulating the required condition for them.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out