We discovered that water coming from a faucet has a smooth appearance while the flow rate is low, but as the flow rate is raised, voids and disturbances may be detected after reaching a specific value. In such a circumstance, if we add a stream of ink while the flow is smooth, the ink flows without mixing with the other layers, however if we introduce it when the flow is turbulent, the ink layer mixes with the other layers of water. This article will teach us about the first kind, which is the streamline, laminar or turbulent flow.
What is Streamline?
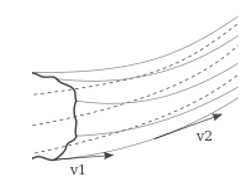
A streamline is the route taken by fluid particles under steady-flow conditions. If the flow lines are represented as curves, the tangent at any point on the curve indicates the direction of the fluid velocity at that location. The curves, as seen in the image below, represent how the fluid particles travel with respect to time.
The curve depicts the steady-state movement of fluid particles. This map is time-stationary, which implies that every particle that passes through a spot acts exactly like the particle before it.
Streamline Flow
Streamline flow in fluids is defined as a flow in which fluids flow in parallel layers with no interruption or mixing, and the velocity of each fluid particle passing by remains constant throughout time at a certain place.
At low fluid velocities, there are no turbulent velocity changes, and the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing. The fluid particles move in a precise sequence relative to the particles flowing in a straight line parallel to the pipe wall, causing the contiguous layers to slide past each other like playing cards.
Turbulent Flow
In contrast to laminar flow, which flows in clean channels or layers, turbulent flow is a form of fluid (gas or liquid) movement in which the fluid experiences random fluctuations or mixing. In turbulent flow, the speed of the fluid at a given spot is constantly changing in magnitude and direction.
However even the currents are mild, wind’s movement and river’s movement is often tumultuous in this sense. The air or water swirls and eddies as the majority of it goes in a certain direction.
Except for laminar flow near the leading edge of solids moving relative to fluids or extremely close to solid surfaces, such as the interior wall of a pipe, or fluids of high viscosity (relatively considerable sluggishness) flowing slowly through narrow channels, most fluid flows are turbulent. Blood flow in arteries, oil transport in pipelines, lava flow, atmosphere and ocean currents, flow through pumps and turbines, and flow in boat wakes and around aircraft wing tips are all examples of turbulent flow.
The Reynolds Number
The Reynolds number is a dimensionless variable that indicates whether a flow pattern in a pipe is laminar or turbulent. We can determine the Reynolds number by the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces.
The Reynolds number formula is as follows:
Re = (p × V × D) / u
Where,
The Reynolds number is Re, the density of the fluid is p, the velocity of flow is V, the diameter of the pipe is D, and the viscosity of the fluid is u.
Important Points
- When viscous forces are dominant (low Re, slow flow), they are sufficient to keep all fluid particles in line, and the flow is laminar.
- Turbulent flow occurs when inertial forces outweigh viscous forces (when the fluid flows faster and Re is greater).
- One of the characteristic numbers used to forecast whether a flow state would be laminar or turbulent is the Reynolds number.
- V is the mean flow velocity, D is a typical linear dimension, fluid density, dynamic viscosity, and v kinematic viscosity are all part of the Reynolds number.
- Turbulent flow occurs when Re exceeds 4000.
- A greater velocity flow is usually necessary, however this also depends on the size of the item.
- The flow is distinguished by the uneven movement of fluid particles. The average motion is in the flow direction.
- The turbulent flow velocity profile is reasonably flat over the central part of a pipe and dips dramatically exceptionally near to the walls. The average flow velocity is about equal to the velocity at the pipe’s center.
- Mathematical analysis is a difficult task. CFD analysis is the primary tool for analysing turbulent flows.
Conclusion
In such a circumstance, if we add a stream of ink while the flow is smooth, the ink flows without mixing with the other layers, however if we introduce it when the flow is turbulent, the ink layer mixes with the other layers of water. In turbulent flow, the speed of the fluid at a given spot is constantly changing in magnitude and direction. However, Reynolds number is a dimensionless variable that indicates whether a flow pattern in a pipe is laminar or turbulent. One of the characteristic numbers used to forecast whether a flow state would be laminar or turbulent is the Reynolds number.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out