Neurons are the little switches that allow you to think and remember things. Your brain has roughly 100 billion neurons. In addition, computers have billions of tiny “brain cells.” They’re known as transistors and are constructed of silicon, a chemical element abundant in sand. Transistors have transformed electronics since their invention by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley over half a century ago.
A transistor is both simple and complicated. Let’s begin with the simple stuff. A transistor is a small electronic component that can perform two tasks. It can function as both an amplifier and a switch:
When used as an amplifier, it accepts a very little electric current (input current) at one end and produces a considerably larger electric current (output current) at the other. To put it another way, it’s a current booster. This is especially beneficial in hearing aids, which were one of the original applications for transistors. A tiny microphone in a hearing aid gathers up noises from the environment and converts them into fluctuating electric currents.
“If you tie a bale of hay to the tail of a mule, strike a match, and light the bale of hay on fire, and then compare the energy wasted by the mule with the energy expended by yourself striking the match, you will comprehend the concept of amplification.”
A modest electric current passing through one area of a transistor can cause a much bigger current to run through another section of the transistor. To put it another way, the little current causes the larger current to activate. All computer chips perform this basic function. A memory chip, for example, contains hundreds of millions, if not billions, of transistors, each of which may be turned on or off independently.
Each transistor can hold two different numbers, zero and one, because it can be in two different states. A chip can hold billions of zeros and ones, as well as almost as many regular numbers and letters, thanks to its billions of transistors (or characters, as we call them). In a moment, I’ll tell you more about this.
Transistor Working diagram
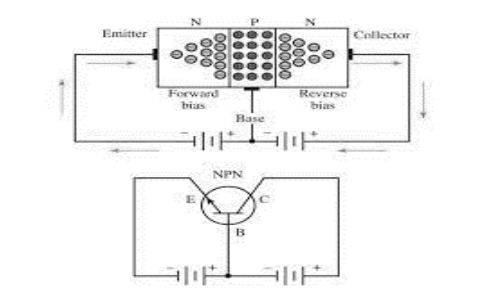
Silicon is commonly used to make transistors due to its high voltage rating, higher current, and lower temperature sensitivity. Because the emitter-base portion is forward biased, the base current passes via the base area. The magnitude of the base current is quite small. As a result of the base current, electrons move into the collector region or generate a hole in the base region.
What is Transistor and its Symbol
A transistor is an electronic component that may be used to amplify or switch electrical signals or power in circuits, allowing it to be employed in a variety of electronic devices. Emitter, base, and collector are the three terminals. A transistor’s core concept is that it allows you to control the flow of current through one channel by adjusting the intensity of a much smaller current flowing through another channel.
The two types of transistors are NPN transistors and PNP transistors. NPN transistors are made up of two n-type semiconductor material blocks and one P-type semiconductor material block. In contrast, PNP transistors have one layer of N-type material and two layers of P-type material. In the diagram below, the symbols for NPN and PNP are shown
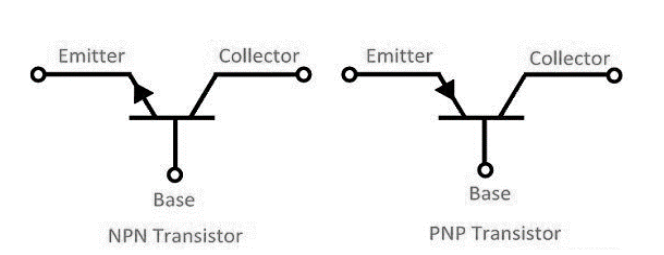
With forward biassing applied to the emitter-base junction, the arrow in the symbol represents the direction of conventional current flow in the emitter. The only difference between an NPN and a PNP transistor is the current direction.
Conclusion
The study of the interplay of physical mechanisms in ferrite-semiconductor systems yields the following results:
- On bipolar and field transistors of various sorts.
- In continuous and pulse modes, at low, moderate, and high level capacity.
- Across a wide frequency range (VHF, UHF, MWF, EHF, HHF).
- Signals of various types and spectra (regular, pseudo-noise, noise, as multipurpose synthesizers of frequencies).
- For ferrite micro-resonators of various sorts and their orientations under an external magnetic field.
- A signal of the basic frequency can be generated in a variety of ways, including amplification, multiplication, division, and frequency modulation.
- Small values of a magnetic induction vector and a mechanical displacement vector are registered.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






