It is a fact that a static electric field encloses a positive or negative charge and that a flow of energy tube or flux exists inside that static electric field. The electric charge radiates or emanates this flux. The magnitude of this flux flow is determined by the amount of charge emitted. The Gauss theorem was established to determine this relationship. In this article, we will understand the meaning of the Gauss theorem and understand its basic principles.
The Meaning of Gauss Theorem
According to the Gauss theorem, the total electric flow through any closed surface around a charge is equal to the net positive charge encompassed by that surface. As a result, the net flux across a closed surface is proportional to the net charge in the closed surface’s volume. The Gauss theorem can be represented as:
Φ = → E.d → A = qnet/ε0
By using this equation, the amount of flux through the surface in the surrounding area can be calculated. The net electric flow stays 0 if no charges are enclosed by a surface. The number of electric field lines entering the surface equals the number of field lines that are leaving the surface.
It can also be mathematically expressed as:
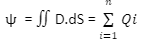
Where the charges are Q1, Q2, Qi, Qn:
D is the flux density in coulombs/m2.
dS is the outwardly directed vector.
Explanation of Gauss’ Theorem
The Gauss theorem can be explained through the following example:
Let us take Q as the charge at the centre of a sphere, and the charge’s flux is normal to the surface. According to the Gauss theorem, the total flux emitted by the charge will be equal to Q coulombs, which can also be demonstrated mathematically. But what happens if the charge is not placed in the middle but rather somewhere else?
In such cases, flux lines are not normal to the surface around the charge at that time. Thus, the flux is resolved into two perpendicular components:
- the horizontal component is the sin component
- the vertical component is the cos component
When all of these components are added up for all of the charges, the net result equals the total charge of the system, proving Gauss’ theorem.
Proof of Gauss’ Theorem
To prove Gauss’s theorem, let us assume a homogeneous isotropic medium of permittivity ε containing a charge Q.

Thus, the equation of flux through the area is:

Important Points in the Gauss Theorem
To understand the meaning of the Gauss theorem, the following points must be kept in mind:
- Factors affecting the value of φ:
- The number of charges contained within a closed surface
- Charges confined by a closed surface and their nature
- The medium of the closed surface
Thus:
φ= ∑q/ε0 for air
φ= ∑q/ε for any other medium
- Factors not affecting the value of φ:
- The charge distribution in the closed surface
- The size of a closed surface’s shape and the area it encloses
- The charge that is present outside the closed surface
- The value of flux with respect to one coulomb is 1/ε0.
- The flux leaving the surface is considered positive, while the flux entering the surface is considered negative.
- Similarly, if the net charge is positive, it indicates that the flux will flow outwards. And if the net charge is negative, it indicates that the flux will flow inwards.
- If the net charge in the closed surface is zero, say ∑q is zero, then φ = 0. For example, if there are one or more dipoles in any closed surface, then φ = 0.
- If φ = 0 then:
(a) Σq = 0 or E = 0 and
(b) E & dA are perpendicular - If the ‘q’ charge is maintained in the cube’s centre, the total flux from the cube will be:
φ = ∑q/0
While the flux from the cube’s face will be:
φ’= ∑q/60
- Similarly, if the ‘q’ charge is kept at one corner of the cube, then the flux from each face will be:
φ’= ∑q/240
Conclusion
Thus in this article, we have learned the meaning of the Gauss theorem. Gauss theorem indicates that the total electric flow through any closed surface around a charge is equal to the net positive charge encompassed by that surface. Furthermore, the sources (positive charges) and sinks (negative charges) of the electric fields encompassed by the surface are the only sources (positive charges) and sinks (negative charges) of the electric flow from any closed surface.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






