Introduction to diamond structure
Diamond is the hardest mineral, consisting of carbon. Diamonds are naturally occurring solid forms of carbon with atoms grouped in a diamond cubic crystal structure. In a diamond, each carbon atom is surrounded by four other carbon atoms linked together by covalent bonds.
Diamond has a crystallographic and cubic structure. The crystal form of diamond is an FCC or face-centred lattice. A lattice is an organised set of points that define the structure of crystal-forming particles. There are three types of lattice structures- face-centred (FCC), body-centred (BCC) and hexagonal closest packed (HCP).
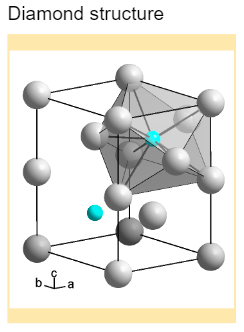
In diamond, each carbon atom is connected with four other carbon atoms by strong chemical bonds, thus making a tetrahedron structure. The hybridisation of the carbon atom is sp3 hybridisation. Diamond has a three-dimensional network with a strong covalent bond.
Cubic structure is the most common crystal structure found in diamonds. In the structure, the unit cells, which are repeating units formed in the lattice, are packed together. There are eighteen atoms present- the atoms present in the corner share eight unit cells, and the atoms in the centre share two unit cells. The total number of atoms is eight per unit cell. The length of each side of the unit cell is 3.567 angstroms and is denoted by a.
Properties of diamond
Physical properties
Crystal structure: Diamond is present in the crystal form of carbon. It is formed in the FCC or face-centred crystal lattice.
Crystal habit: Diamond is present in the euhedral or octahedral form. The crystal structure of diamond has a cubic arrangement. The crystals have round-off edges.
Types of diamonds
Diamonds are categorised into five types based on presence and level of purity:
- Type la
- Type lb
- Type 1ab
- Type lla
- Type llb
Mechanical properties
Hardness: Diamond is the hardest of all natural minerals. Its hardness depends on its purity.
Elasticity: Diamonds normally have a non-elastic in bulk form. Any tension can fracture it. However, single-crystalline diamonds are elastic and can be stretched.
Yield strength: The yield strength of diamond is 128 to 140 Gpa.
Conductivity: Diamond is a good electrical insulator as well as a semiconductor.
Surface property: Diamond is hydrophobic and lipophilic in nature.
Chemical property: At room temperature, diamond does not interact with any chemical reagent, even with strong acids and bases.
Uses or application of diamond
Jewellery
Diamonds are most commonly used in ornaments like rings, neckless, earrings, etc. In the gem industry, the value of diamonds is very high.
Industrial Uses
In various industries, diamonds are used for their hardness and thermal conductivity. Common applications include glass cutting and tools for cutting and grinding.
Pharmaceuticals
Diamonds are used in making medicines and beauty products. They are also used in making medical tools, like tools used in cataract surgery.
Conclusion
Diamond is a mineral composed of carbon. It has a crystal lattice form. Each carbon atom in a diamond is attached to four other carbon atoms. Diamonds are categorised into five categories based on the level of purity. Due to its various properties, it is widely used in making jewellery, medicines, cutting and grinding tools.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






