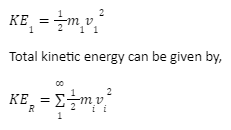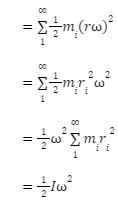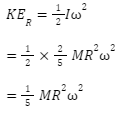Moment of Inertia
A system’s moment of inertia is a measurement of how difficult it is to modify an object’s rotational motion around a certain axis. It is a metric for a system’s rotational inertia. The moment of inertia of a rotating object is determined by the mass of the object as well as the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia increases when the mass is dispersed further away from the axis, making it more difficult to adjust the rotational motion. For different bodies, the moment of inertia has varying values.
kg m2 is the SI unit for moment of inertia (which is consistent with our notion that it depends on mass and square of the distance from the rotational axis).
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational kinetic energy is the energy that an object has when it spins around an axis. A rotating body’s kinetic energy is similar to linear kinetic energy and is determined by the following factors:
The energy is proportional to the speed at which the thing rotates. The faster the object rotates, the more energy it has.
The angular kinetic energy of a rotating object is proportional to its mass.
The energy of a point mass is also determined by its distance from the rotating axis. Particles that are farther away from the rotation axis have more rotational kinetic energy than those that are closer to it.
Formula of Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational kinetic energy has a formula that is similar to linear kinetic energy. We know that 12mv2 is the linear kinetic energy of a mass m travelling at speed v . The stiff body can be assumed to be made up of an infinite number of point masses. Each point mass will be travelling with a linear velocity equal to the tangential velocity of that point at any given time. The magnitude of tangential velocity at any location r from the rotating axis of a rigid body rotating with angular velocity ω can be calculated as follows:
v=rω
The kinetic energy of a rigid body with any point mass m1 is given by,
KER=12I2 is the rotational kinetic energy. The rotational mass or moment of inertia of a rotating object is denoted by I, while the angular velocity is denoted by .
Joule (J) is the SI unit for rotational kinetic energy.
Dimensional Formula of Rotational Kinetic energy
We know that KER=12I2 is the formula for rotational kinetic energy. Any object with a mass of m has a moment of inertia with the parameters mr2. [I]=M1L2T0 is now the dimensional formula for the moment of inertia.
Also, the angular velocity dimensional formula [ω]=M0 L0T-1.
By plugging in the moment of inertia’s dimensional formula and angular velocity, we get:
Dimensional formula of rotational kinetic energy, [KER]=M1L2T-2, which is the same as that of energy.
Kinetic Energy of a Rigid Body in both Rotational & Translational Motion
When the body rotates and moves in both directions, it generates both translational and rotational kinetic energy.
KET=1/2mv2COM is the translational kinetic energy. vCOM is the translational velocity of the body’s centre of mass.
KER=1/2ICOM2 is the rotational kinetic energy. The moment of inertia of the rigid body about its rotational axis is denoted by ICOM .
As a result, the stiff body’s total kinetic energy will be
KE=1/2mv2COM+1/2ICOM2
Rotational Kinetic Energy using Angular Momentum
We know that L=Iω is the angular momentum of a rigid body with a moment of inertia I rotating with angular speed .
The rotational kinetic energy is:

Rotational Kinetic Energy Formula for a Sphere
We know that a solid sphere’s moment of inertia around an axis passing through its centre is given by I=25 MR2 . The radius of the solid sphere is R, and the mass of the solid sphere is M.
The sphere’s rotating kinetic energy is given by,
As a result, the rotational kinetic energy of a solid sphere spinning around a fixed axis passing through its centre of mass is equal to
KER=1/5 MR22
Applications of the Rotational Kinetic Energy
The Rotational Energy formula has a wide range of applications and can be used to:
Calculate the basic kinetic energy of a rotating object.
Calculate the kinetic energy of a rolling item, which includes both rotational and translational kinetic energies.
Conclusion
There are two types of energy in a rigid body: kinetic energy and potential energy. The potential energy of a rigid body is the energy stored in the body as a result of its position and other stressors. A rigid body’s kinetic energy is a type of energy possessed by a moving body as a result of its motion. When an item is worked on by applying a net force, it gains speed, which increases its kinetic energy. The mass and speed of a moving body determine its kinetic energy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out