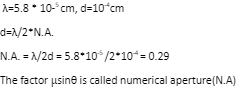The radiation of light shows a dual nature that is wave and particle. Phenomenon like diffraction, interference and polarization can be explained on the basis of wave nature of light whereas phenomenon as like Photoelectric effect, Compton effect etc. can be explained only in terms of quantum theory of light. (Quantum theory of light states that light is a composition of small packets known as photons and have wave-like properties).
Dual nature of radiation and matter
Material particles when in motion shows wave like properties this theory was given by de- broglie and squall dual nature of matter. His reasoning was based on two facts:
- Mass in energy are the two physical quantities which have all the physical forms of the universe. Einstein’s mass energy relationship shows that matter(mass) and energy(radiation) has balanced proportion i.e. E=mc2.
- Since, radiation has dual nature therefore according to mass energy relationships must also possess dual nature. The particles like electron, proton and neutron should not only behave like mask points but they should also have wave nature when they are in motion.
de- Broglie Wave equation
Let us consider a Photon as an Electromagnetic wave of frequency(ѵ) so its energy from Planck’s Quantum theory is given by:- E=hѵ…1
h- Planck’s Constant
Constructive Photon as a particle of mass m, then energy associated with this particle is given by Einstein mass energy relationship,

Inference of de-broglie equation
- The wavelength of a moving particle is inversely proportional to its momentum.
λ ∝ 1/p.
- If v=0 then λ= ∞ Waves are associated with a material particle when they are in motion.
- To be a part of the de- broglie wave a particle needs to have a charge. That’s why de Broglie wave or also known as matter waves.
- Broccoli waves can never be electromagnetic in nature as electromagnetic waves are associated with accelerated charged particles only
de- Broglie wavelength of an electron
Let us consider an electron of mass m and charge e.
v = final velocity attained by electron when it is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of V volts
kinetic energy = work done on electron by electric field

Conclusion
We have learnt that every form of physical universe is a combination of two physical quantities that is mass and energy. As we can see in Einstein’s mass energy relationship E = mc2. It states the mutual symmetry between matter(mass) and radiation(energy).The waves associated with matter particles in motion are called de- broglie waves and their wavelength is called de Broglie wavelength. The wavelength associated with a moving particle is related to its momentum. The de-broglie equation shows the dualism of matter, that is it contains waves and particles. de-broglie wavelength is independent of the charge and nature of the material particle. It significantly measures only in case of subatomic particles like electrons, protons etc because their masses are very small. However it is indeed very small, quite beyond measurement. The wavelength of the matter wave was given by λ=h/p.
de – broglie wavelength λ=h/p=h/mv
de – broglie wavelength of an electron λ=h/√2meV
K.E = 1/2mv2 = p/2m, momentum p=√2mK
Units used – Wavelength λ is in meters, velocity v in ms-1, momentum p in kg ms-1, potential difference V in volt.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out