Straight-line motion is also known as rectilinear motion. The movement of a particle or a body is described by this type of motion.A body is considered to move rectilinearly if any two of its particles travel the same distance along two parallel straight lines. The diagrams below depict rectilinear motion for a particle and a body.
![]() Quantities involved:
Quantities involved:
Distance:
The entire distance travelled by the travelling object/particle. For instance, if an object moves 10 metres forward and 6 metres backward, the total distance travelled is 10+6 = 16 metres.
Displacement is defined as the NET distance between the starting and ending points of motion. Using the same example as before, if the body walks 10 m ahead and 6 m backward, it is only (10-6) m from the beginning place. As a result, the displacement is only 4 metres.
The rate of change of displacement is defined as velocity (v). It has a purpose. This direction is denoted by a positive or negative sign in linear motion.The boldface indicates the fact that it has a direction.
Average velocity:It is given by the displacement s2–s1 divided by the overall time interval (t2–t1) it covers.
Instantaneous velocity:When the time interval reaches zero, the average velocity reaches its limit. It gives the velocity of an object at a given point in time.
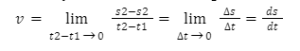
As a result, it is the displacement’s time derivative.
Speed:The magnitude of velocity is represented by speed (v). As a result, it has no meaning and is always non-negative. It is not written in boldface, unlike velocity, because it has no direction.
Acceleration:The rate of change of velocity with respect to time is defined as acceleration. Acceleration is the second derivative of displacement, which can be calculated by differentiating position with respect to time twice or velocity with respect to time once.
Rectilinear motion 10 examples:
Fruit is falling off the tree
As the fruit ripens, it becomes separated and falls to the ground; and even when a strong wind blows, numerous fruits fall to the ground surrounding the tree.
As the fruit separates from the node of a branch of a tree, it falls linearly towards the earth due to the gravitational force of attraction.
Marching
You must have observed a group of soldiers walking on the ground or marched during the event. The speed of soldier marches in a row remains consistent during the marching exercise, demonstrating uniform rectilinear motion.
Bowling
A ball launched from a great height follows a route towards the bowling pins based on the force used to accelerate the bowling ball’s centre of mass. The bowling ball will follow a path to collide with the bowling pins when it is hurled towards the pins.
Running
While running, we either maintain a constant speed or alter it accordingly. If a person running in a rectilinear motion on a stadium maintains a constant speed at every interval of time, that person is said to be in a uniform rectilinear motion.
Load Pushing
A man pushes a 45kg burden and displaces it at a speed of one metre per second. A force is supplied to the object to drag it every one metre in one second, so that the displacement of the object remains constant throughout, and the object is said to be in uniform rectilinear motion.
Sliding a Boulder
A boulder falling downhill follows a nearly straight sloped path to the horizontal surface. A boulder’s velocity increases gradually and eventually slows as it approaches the horizontal surface. When we plot velocity versus time on a graph, we will trace a parabolic curve.
Arrow Hitting the target
An arrow fired by an archer travels in a straight line until it strikes its target. It travels through the medium with the speed of an arrow, which gradually decreases as it follows the rectilinear motion.
A car is driving down the road
An automobile moving on a road that accelerates at a steady rate or changes velocity is also an example of rectilinear motion.
Rectilinear motion question example:
Q.A particle travels half the total distance with speed v1 and the other half with speed v2 along an arc. What is the particle’s average speed?
A.Let the particle’s total distance travelled be 2s.
Time spent travelling in the first half = S/V1
Time spent travelling in the second half =S/V2
Average speed = total distance covered / total time taken

Conclusion:
Linear motion is the most fundamental type of motion. Objects that do not experience any net force will continue to move in a straight line with a constant velocity until they are subjected to a net force, according to Newton’s first law of motion. External forces such as gravity and friction can cause an object’s motion to change direction in everyday situations, therefore its motion cannot be defined as linear.Linear motion can be compared to general motion. In general motion, vectors with magnitude and direction define a particle’s position and velocity.
The orientations of all the vectors defining the system are equal and constant in linear motion, which means that the objects travel along the same axis and do not change direction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






