Rectifiers include vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers, and various silicon-based semiconductor switches.Even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator combinations have been employed in the past. To serve as a point-contact rectifier or “crystal detector,” early radio receivers, known as crystal radios, used a “cat’s whisker” of tiny wire pushing on a crystal of galena (lead sulphide). The technique is known as rectification because it “straightens” the current course.
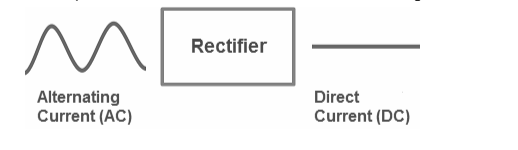
Rectifier definition:
Forward biased:
The diode is said to be forward biassed when a voltage is applied to it in such a way that the positive terminal of the battery is linked to the p-type semiconductor and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the n-type semiconductor. When this forward bias voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode, a large number of free electrons (majority carriers) in the n-type semiconductor are repelled by the battery’s negative terminal, while a large number of holes (majority carriers) in the p-type semiconductor are repelled by the battery’s positive terminal.
As a result, free electrons in the n-type semiconductor begin to move from the n-side to the p-side, and holes in the p-type semiconductor begin to move from the p-side to the n-side.
We already know that electric current denotes the movement of charge carriers (free electrons and holes). As a result, the movement of electrons from the n-side to the p-side and the flow of holes from the p-side to the n-side both conduct electric current. In a forward bias condition, the majority carriers generate the electric current. As a result, the electric current produced in a forward bias condition is also referred to as majority current.
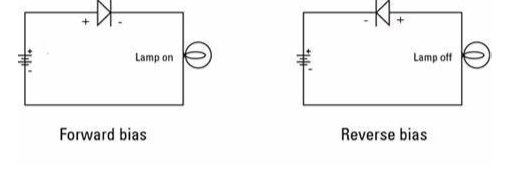
Reverse biased:
When a voltage is provided to the diode in such a way that the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the n-type semiconductor and the negative terminal to p-type semiconductor.
When this reverse bias voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode, a large number of free electrons (majority carriers) in the n-type semiconductor are attracted by the positive terminal of the battery, while a large number of holes (majority carriers) in the p-type semiconductor are attracted by the negative terminal of the battery.
As a result, the free electrons (majority carriers) in the n-type semiconductor are drawn to the positive terminal of the battery, whereas the holes (majority carriers) in the p-type semiconductor are attracted to the negative terminal.
Rectifier Working:
Rectifiers are primarily divided into two types:
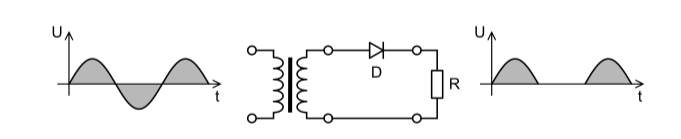
Half wave rectifier:
The half wave rectifier, as the name implies, is a form of rectifier that converts half of the AC input signal (positive half cycle) into pulsating DC output signal while blocking or losing the remaining half signal (negative half cycle).
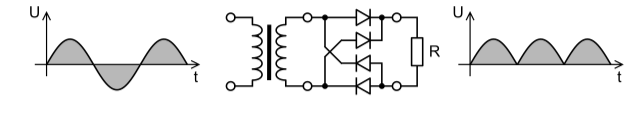
Full wave rectifier:
The full wave rectifier is a type of rectifier that converts the complete alternating current input signal (positive and negative half cycles) to a pulsing direct current output signal. Unlike a half-wave rectifier, the input signal in a full-wave rectifier is not wasted. In mathematics, this corresponds to the absolute value function. Full-wave rectification converts the input waveform’s two polarities to pulsating DC (direct current), resulting in a higher average output voltage.Two diodes plus a center-tapped transformer are required, or four diodes in a bridge setup with any AC supply (including a transformer without a centre tap). Single semiconductor diodes, double diodes with a common cathode or common anode, and four- or six-diode bridges are constructed as standalone components.
Rectifier uses:
The basic function of rectifiers is to generate DC power from an alternating current supply (AC to DC converter). Rectifiers are found in almost all electronic equipment’s power supplies. Linear power supplies and switched-mode power supplies are the two basic categories of AC/DC power supplies. In such power supplies, the rectifier will be connected in series with the transformer, followed by a smoothing filter and perhaps a voltage regulator.
Converting DC power from one voltage to another is significantly more difficult. One technique of DC-to-DC conversion first transforms power to AC (through an inverter), then changes the voltage using a transformer, and then rectifies power back to DC.
A frequency of several tens of kilohertz is often utilised since it requires much less inductance than lower frequencies and eliminates the need for heavy, bulky, and expensive iron-cored components. Another method of converting DC voltages is to utilise a charge pump, which uses quick switching to alter the connections of capacitors; however, due to the size of the capacitors used, this technique is normally restricted to supply up to a couple of watts.
Conclusion:
Vacuum tube thermionic diodes and copper oxide- or selenium-based metal rectifier stacks were employed prior to the development of silicon semiconductor rectifiers. Except for a few vacuum tube audio enthusiasts, vacuum tube rectifiers became useless with the development of silicon circuitry. Semiconductors of various varieties (junction diodes, Schottky diodes, etc.) are frequently utilised for power rectification from very low to very high current.Other devices with control electrodes that also function as unidirectional current valves are employed when more than simple rectification is required, such as variable output voltage. High-power rectifiers, such as those used in high-voltage direct current power transmission, make use of a variety of silicon semiconductor devices
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






