Introduction:
What is Projectile Motion? As the name suggests, projectile motion is the movement of an object that is launched into the air. Given the initial velocity and angle of projection, it is a problem that has been studied since ancient times. The solution is not obvious and can be approached in various ways. Galileo was one of the first people to have ever described projectile motion. This article will go through a basic introduction of Projectile Motion, it’s important terms and definitions, projectile motion equations, applications, and formulae.
Body:
Gravity is the most important force at work when a projectile is involved. Other forces are also at play, but they have a negligible impact compared to gravity. A projectile’s trajectory is the path it takes as it travels through space. A baseball hit by a bat or thrown by a player is an example of a projectile.
Parabolic Projectile Motion
Consider the following scenario: a ball is projected at some angle with the horizontal x-axis with an initial velocity of u.
The point of projection is considered as origin; the projection angle is θ; the distance travelled by the projectile along the x-axis is called Horizontal Range, often known as simply Range. The time it takes for a particle to travel from the point of origin to the surface is called flight time.
To determine various parameters associated with projectile motion, it is possible to employ differential equations of motion:
v = u + g t (where g represents vector quantity)
s = u t + 12g t²
v² = u² + 2g.s ( g.s represents dot product of the two vectors)
( For the sake of simplicity let ‘g’ represent the magnitude of g or |g|)
Here,
u is the initial velocity
g is the acceleration due to gravity
t is the time
s is the displacement
v is the final velocity
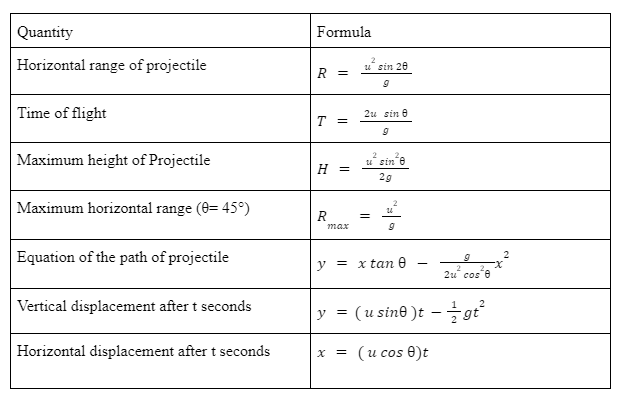
Total time of flight
In the vertical direction, the resultant displacement (s) equals zero. Therefore, the following equation calculates the time of flight formula.
Total time of flight(T) = 2using
Horizontal Range
The horizontal range is equal to the horizontal component of velocity multiplied by the total flight time (T)
R= u cosθ 2u sin/g
Therefore, in a projectile motion, the horizontal range is given by (R):
Horizontal range(R) = u²sin2g
Projectile’s Maximum Height
After establishing what a projectile is and what projectile motion is, we should determine the maximum elevation. The highest vertical position along the object’s trajectory corresponds to the maximum height reached. The projectile’s horizontal displacement is referred to as the projectile’s range in this context. The beginning velocity of the object affects the range of the projectile.
u denotes the starting velocity, g represents the acceleration due to gravity, and H is the maximum height in metres, where θ indicates the angle of the initial velocity with the horizontal plane.
The formula for calculating the Projectile’s Maximum Height is as follows:
H = u²sin² θ 2g
Important Points Related to Projectile Motion
- At the highest point, linear momentum is m(u cos θ), and the kinetic energy is 12m(u cosθ)2.
- The projectile has a parabolic path.
- At the starting point, Kinetic energy= 12mu2
- At the starting point, Linear momentum= mu
Important Formula Related to Projectile
Projectile Motion Application
- Throwing a ball or anything:
When a ball is thrown up into the air, we see that it travels for some distance and then falls. This path followed by the object appears to be like a parabola or U-shaped curve. This part of the path is neither linear nor circular; it is called projectile motion, and the path followed by the ball or the object is called its trajectory. So, when we throw a ball horizontally into the air, it does a loop that goes up and over as if going in a parabola-like pattern and then comes back down. This happens because of projectile motion. In physics, particularly mechanics (the study of physical change), an object’s speed is calculated by dividing its distance by how much time; if an object covers 30 meters in two seconds, then it has been travelling at speed 15 meters per second (15 m/s).
- Bullet fired from a gun:
When an object is propelled through the air, the force from the ignition of gunpowder and the force of gravity combine to influence how long and in what direction the bullet travels. However, as soon as the bullet leaves the gun, gravity begins to exert a greater force and begins guiding it towards the Earth. Whether it falls or not depends entirely on how much opposing force is met along its path.
Conclusion
The projectile in physics refers to an object that is in flight after being thrown or projected. In this article, we covered the Introduction of Projectile Motion, its definition, the various important terms you need to know, some very important points related to projectile motion, some important formulas, and lastly, the real-life application of Projectiles.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






