Pressure
If you tried to hammer a bowling pin into the wall, the only thing that would happen is that people would stop lending you their bowling pins. A nail, on the other hand, would be much more likely to pierce the wall if hammered with the same force. This demonstrates that knowing the quantity of a force isn’t always enough: you also need to understand how that force is distributed over the impact surface. All of the force between the wall and the nail was concentrated in a very tiny area on the pointed tip of the nail in the case of the nail. The area touching the wall for the bowling pin, on the other hand, was significantly bigger, and so the force was much less focused.
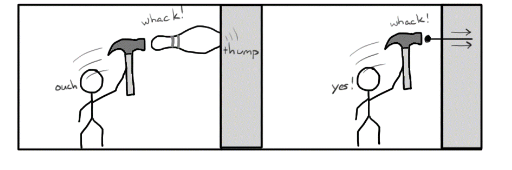
Pressure Equation
The amount of force exerted per area is defined as pressure.
P=F ⁄A
This definition also implies that newtons per square meter, N ⁄m² are the units of pressure, which are also known as pascals or Pa for short.
Velocity
Your velocity motion is most likely similar to the scientific definition. You already know that a significant displacement in a short period of time equals a high velocity, and that velocity is measured in distance divided by time units like miles per hour or kilometers per hour.
Velocity Equation
The change in location divided by the period of transit is how average velocity is calculated.
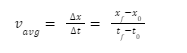
Where, Vavg=average velocity
∆x=change in position
xf and x0= final and start position
at times tf and t0
How Pressure and Velocity are related
When velocity and pressure are stated to be inversely proportional, it means that as pressure rises, velocity decreases, maintaining the algebraic total of potential energy, kinetic energy, and pressure. Pressure reduces in a similar manner as velocity rises. The pace at which an object moves in a certain direction is called velocity. Pressure is the physical and external force exerted or applied to an object.
Bernoulli’s Formula for Pressure and Velocity Relationship
Bernoulli’s equation can be regarded as a fluid-systems version of the energy conservation principle. It is one of the most important and helpful equations in fluid mechanics. In an incompressible inviscid flow, it establishes a link between pressure and velocity.
This is the most well-known equation in fluid dynamics. Bernoulli’s equation, often known as Bernoulli’s effect, describes the qualitative behaviour of a flowing fluid. This effect causes a decline in fluid pressure in places where the flow velocity is increased. This pressure reduction in a flow channel constriction may appear counterintuitive at first, but it becomes less so when the pressure is viewed as energy density. In the high-velocity flow through the constriction, kinetic energy must expand at the price of pressure energy. The dimension of terms in the equation is kinetic energy per unit volume.
Conclusion
One thing that both macroscopic factors that influence many natural occurrences have in common when comparing pressure velocity relations is that they are both macroscopic parameters. Pressure, on the one hand, is a measurement of force per unit area. Velocity, on the other hand, is a measurement of the rate of change in displacement.
The higher the velocity of a fluid (like, liquid or gas), the lower the pressure it exerts. Bernoulli’s Principle is the name for this. The random motion of fluid molecules creates fluid pressure. When the fluid accelerates, some of the energy from the random motion is utilized to propel the fluid faster in its current direction. As a result, the pressure is reduced.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




