The units of force are the Newton and Dyne. Under the International System of Units, a Newton is a derived unit of force (SI Units). It is defined as 1 kgm/s², the force that causes a mass of one kilogram to accelerate at a rate of one metre per second per second. It was named after Isaac Newton in honour of his contributions to classical mechanics, particularly Newton’s second law of motion.
The derived unit of force under the Centimetre-Gram-Second (CGS) units system is the dyne. A Committee of the British Association for the Advancement of Science proposed the word dyne as a CGS unit of force in 1873.
Definition
- One newton is defined as the force required to accelerate one kilogramme of mass one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units “metre per second squared” can be thought of as a change in velocity over time, i.e., a 1 metre per second increase in velocity every second.
The Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) Resolution 2 of 1946 established the MKS system of units’ unit of force as the quantity required to accelerate 1 kilogramme of mass at a rate of 1 metre per second squared. The designation newton was given to this force by the 9th CGPM Resolution 7 in 1948. The MKS system was eventually adopted as the basis for the current SI system of units. In the International System of Units, the newton became the standard unit of force.
Isaac Newton is commemorated with the newton. Its symbol begins with an uppercase letter (N), but when written in full, it follows the capitalization standards for a common word; for example, “newton” is capitalised at the start of a sentence and in titles, but otherwise is lower case.
Newton’s second law of motion asserts, in more formal terms, that the force applied on an object is directly proportional to the acceleration so obtained by that object, namely:
F = m.a
Where, m = mass , a = acceleration of an object
- “The force necessary to accelerate a mass of one gram at a velocity of one centimetre per second squared,” says the dyne. The dyne can also be defined as “that force that, when operating for one second, causes a change in velocity of one centimetre per second in a mass of one gramme.”
In the former metre–ton–second system of units, one dyne equals 10 micronewtons,
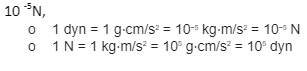
Relation between Newton & Dyne derivation
Both have been identified as force units in two different systems. As a result, we can begin by saying –
A newton is the force required to cause an object of mass 1 kg to accelerate at 1 m/s². In maths, it’s written as-
1N=1kg×1m/s²
⇒ 1000 g ×100cm/s²
⇒1000×100×g×m/s²
⇒ 105g cm/s²
Therefore, the final equation for newton and dyne is 1 newton = 10 5 dyne.
CONCLUSION
Force, like pressure or energy, is a quantity that has or may be quantified in a unit. Force units, on the other hand, can differ depending on the measurement system used. Let’s get down to business.
When it comes to physical dimensions, MLT-2 is most commonly used to quantify force. When it comes to practical considerations, the weight of an object is usually taken into account rather than its mass.
In the centimetre-gram-second system of physical units, a dyne is the force required to accelerate a free mass of one gramme by one centimetre per second per second.
In the International System of Units (SI units), a newton is an absolute unit of force. It’s the force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at one metre per second per second. In the centimetre-gram-second (CGS) system, one newton equals 100,000 dynes, while in the foot-pound-second (English, or customary) system, one newton is around 0.2248 pound.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






