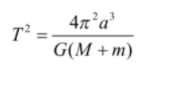The periods, orbits, and regions of the planets and the sun are often central to Kepler’s law of planetary motion. In a sun-centered solar system, the planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun stationary at one point. Based on his analysis of the motions of the planets, Kepler developed a set of rules known as Kepler’s three laws.
Kepler’s three laws determined how the planets behave based on their orbits through space. In 1609, The New Astronomy published Kepler’s first two laws of motion.
There are two types of motion of particles.
Bounded Motion
The particle has limited negative total energy (E < 0) in bounded motion and contains two or more extreme points where the net energy is always equal to the potential energy of the particle which means that the value of kinetic energy is zero.
Eccentricity of 0 ≤ e < 1, E < 0 represents the motion of a body is bounded. The eccentricity is zero for a circular orbit, and the value of eccentricity is 1 (one) for an elliptical orbit.
Unbounded Motion
The total energy of an unbounded motion of a particle is always positive (E>0) which means the value of net energy is always greater than 0 and has a single extreme point where the net energy is equal to the potential energy of the particle which means that the value of kinetic energy is zero.
Eccentricity of e ≥ 1, E > 0 represents motion of the body is free. The value of eccentricity of a parabolic orbit is e = 1, and the value of eccentricity of a hyperbolic orbit is e > 1.
Kepler’s Law of Planetary Motion
Kepler gives three laws of planetary motion
Kepler’s First Law — The Law of Orbits
According to Kepler’s First Law, which is also known as the law of ellipses, planets revolve in an elliptical pattern around the sun. Kepler’s first law is commonly known as the law of orbits.
According to the rule, the orbit of each planet is an ellipse around the sun, with the sun at one of the two foci of the ellipse.
The planets revolve around the sun in a circular orbit that we already know. However, according to Kepler, the planets revolve around the sun, not in a circular orbit. But it is centered on an ellipse.
Ellipse has two foci (S and S’). The Sun (S) is in one of the foci of the ellipse. Perihelion (PS) is the point where the planet is closest to the Sun, while aphelion (AS) refers to the point where the planet is furthest from the Sun. Let Major axis is (2a) and minor axis is (2b). The sum of a planet’s distances from two foci is fixed, which is one of the properties of an ellipse. The seasons are caused by a planet’s elliptical orbit.
Kepler’s Second Law — The Law of Areas
Kepler’s second law, commonly known as the law of area, calculates the speed at which each planet rotates as it orbits the sun. The rate or speed at which each planet spins through space is constantly changing. When a planet is closest to the sun, it spins fastest, and when it is farthest from the sun, it spins slowest.
Kepler’s second law states that orbiting satellites will accelerate when they approach the focus. Because the orbiting object comes near the object pushing it into the orbital path, the effect of gravitational force on it increases.
The area which is covered by the planet or rotating object in the given time, according to the mathematical formulation of the law, is the same regardless of the distance to the object at focus. As the areas are similar or equal, the farther arc is shorter, which results in a slow speed. This applies to all objects in orbit.
Kepler’s Third Law – The Law of Periods
According to Kepler’s third law or Kepler’s law of periods, “the square of orbital period of a planet in an elliptical orbit around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis”.
Therefore,
The third law of Kepler, which is often known as the law of the Period Law, sets a comparison of the orbital period of a planet and the radius of orbit to those of other planets.
The third law compares the motional properties of multiple planets, in contrast to Kepler’s first and second laws, which describe the motional properties of a single planet.
The general form of Kepler’s third law is derived from Newton’s Law of gravitation which is given as
Here,
T = time period
G = gravitational constant
M = mass of sun
m = mass of planet
a = length of semi major axis
Conclusion
Kepler’s three laws determined how the planets behave based on their orbits through space.
According to Kepler’s First Law, which is also known as the law of ellipses, planets revolve in an elliptical pattern around the sun.
Kepler’s second law states that orbiting satellites will accelerate when they approach the focus.
According to Kepler’s third law or Kepler’s law of periods, “the square of orbital period of a planet in an elliptical orbit around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis”.
Therefore,
The general form of Kepler’s third law is derived from Newton’s Law of gravitation which is given as
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out