We know that integration is an important part of calculations, and it is done using various methods. Of all the methods used for integration, integration by a partial fraction is one of the methods. In this, the complex rational fractions are converted into partial fractions, which are in the simpler form using the formulas for decomposition of rational fractions into a partial fraction. Then, the integration is carried out. Let’s look at working with the complex rational fraction to carry out their integration by partial fractions.
Definition of partial fraction
If any algebraic equation in the form of fractions is complex, then it is divided into fractions or simpler parts. These simpler parts are called partial fractions. For example, 6/8 can be divided into 1/4+1/2, in the same way, we can divide the complex rational fraction into the simpler fraction, let us assume that we have,
2/(x+1) – 1/x
on adding, we will get
2/(x+1) – 1/x = (x-1)/(x2+x).
Now if we have
(x-1)/(x2+x)
so we can decompose it into
(x-1)/(x2+x) = 2/(x+1) – 1/x
From the above, we can see that the partial fraction is converted into a simple fraction. Thus it would be easy to integrate this fraction. Thus, integration by partial fractions will be,
∫[f(x)/g(x)]dx = ∫[p(x)/q(x)]dx + ∫[r(x)/s(x)]dx
Where , f(x)/g(x) = p(x)/q(x) + r(x)/s(x) and
g(x) = q(x).s(x)
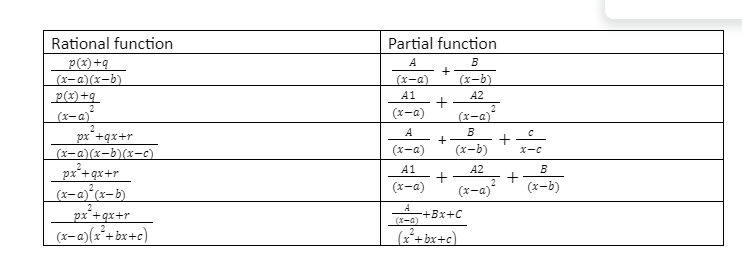
Rules to decompose rational fractions to Partial Fractions
Below are the formulas which can be used to divide the rational fraction into partial fractions, which are easier to integrat
![]() In what cases does the partial fraction work?
In what cases does the partial fraction work?
In the case of the proper rational fraction, we can directly do the partial fraction. In the case of the improper rational fraction, you have to divide it into the proper rational fraction (can be done with the help of the polynomial long division method).
Integration by Partial Fraction (Notes).
Integration by a partial fraction can be done easily if you understand it. Let us take an example under the integration process by a partial fraction.
Let’s take, ∫[6/(x2-1)]dx
By the formula: x2-1 = (x+1)(x-1)
By using the formula in the equation we get:
∫[6/(x2-1)]dx = ∫[6/(x+1)(x-1)]dx
By using the formula of partial fraction for this kind of rational form, we get:
6/(x+1)(x-1) = A/(x-1) + B/(x+1)
Now, we need to find the value of A and B by making a common denominator on both sides.
6/(x+1)(x-1) = [A/(x-1)][(x+1)/(x+1)] + [B/(x+1)][(x-1)/(x-1)]
6/(x+1)(x-1)= [A(x+1) + B (x-1)]/(x-1)(x+1)
We have got the denominators equal to the denominators on both sides so the numerators will also be equal.
6 = [A(x+1) + B (x-1)]
On solving we get,
A = 3, and B = -3
Hence, we can write
6/(x+1)(x-1) = 3/(x-1) + (-3)/(x+1)
Now, we can write:
∫[6/(x2-1)]dx = ∫[3/(x-1) – 3/(x+1)]dx
On solving, we will get:
∫[6/(x2-1)]dx = −3ln(|x+1|)+3ln(|x−1|)+C
Tip to solve the Partial fraction.
If you have a proper fraction, then start with it, but if you have an improper fraction, you have to divide it between making it proper.
The bottom must be factored into linear factors.
After this, write the partial fraction for every factor and write their exponent.
Now, the whole equation has to be multiplied by the bottom.
Substitute zeros to the bottoms to solve the coefficients.
Solved example for Integration by Partial Fraction
Q. ∫xx+23-2xdx
Solution: By using the partial fractions formula,
We can say that, I = ∫xx+23-2xdx
Thus, we get,
A (3 – 2x)+ B(x + 2) = x
Also, we get the following,
3 – 2x=0
Now let’s find the value of x ,
3 = 2x
Therefore, x= 32
And A (0) +B (32+ 2) = 32
On calculation we get,
B (72) = 32 where the value of B = 37
When we further calculate,
Now, when we take x + 2 = 0 where x = -2
A (7)+B(0) = -2
Now, A = -27
we get, ∫xx+23-2xdx=-27 × 1x+2 + 37 × 13-2x
This can be written as, ∫xx+23-2xdx = ∫1x+2 dx + 37∫13-2xdx
Now when we integrate with respect to x,
= -27 log |x + 2|+ 37 × 1-2log|3-2x| + C
So now we get,
=-27log |x + 2|+3-14 log|3 – 2x| + C
Thus above are the partial fractions examples and solutions for integration.
Conclusion
Thus, we can conclude from the above that all the rational fractions are not easy to integrate. Some rational fractions have to be converted into partial form using some formulas to carry out the integration. The improper rational fractions have to be converted into the proper rational fractions by dividing them to carry out the further procedure. In contrast, in the case of proper rational fractions, you can convert them into partial fractions and then carry the integration.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





 In what cases does the partial fraction work?
In what cases does the partial fraction work?
