Many students have trouble grasping the fundamentals of physics. This subject, on the other hand, is not all that tough if mastered through diagrammatic representations. This is due to the fact that diagrams aid in visual learning, which is more successful than memorising things through writing or reading. So, as you work on your board exam preparations, keep practising the crucial Physics diagrams.
Important Physics diagrams
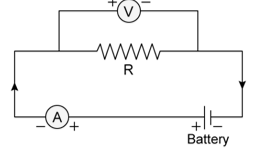
Verification of OHM’s Law
According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference given across it when the temperature remains constant.
V=IR
Here V is the potential difference
I is the current and
R is the Resistance
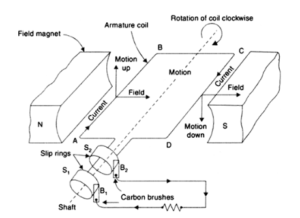
AC Generator
An alternating current generator (AC generator) is a device that converts mechanical energy into an alternating current of electricity. Electromagnetic induction is the principle behind it. When a closed coil is spun in a uniform magnetic field with its axis normal to the magnetic field, the magnetic field lines flowing through the coil shift, creating an induced emf and current flow.
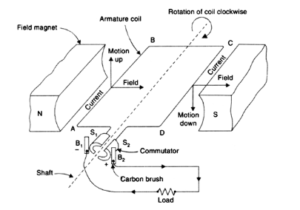
DC generator
A DC generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the direct form. The split ring commutator in the DC generator replaces the slip rings in the AC generator. The split ring commutator is made up of two semi cylindrical brass rings S1 and S2 that are permanently linked to the armature coil’s two ends. The two split rings revolve around the same axis of rotation as the armature coil.
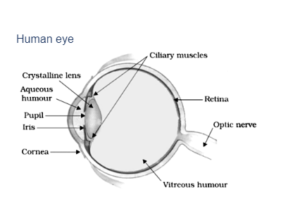
Human eye
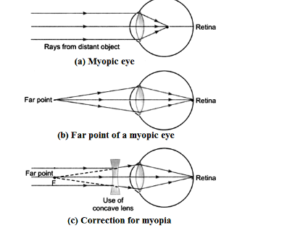
Defects of vision and their correction
Myopia is a vision defect in which a person can clearly see adjacent items but not so clearly perceive far objects. The image is created in front of the retina in this situation.
Myopia can be remedied in such a person’s spectacles by utilising a concave lens with a sufficient focal length.
 Hypermetropia is a vision disorder in which a person may clearly see distant things but not so clearly perceive objects close to them. The image is created behind the retina in this scenario. Hypermetropia can be treated by wearing spectacles with a convex lens of a sufficient focal length.
Hypermetropia is a vision disorder in which a person may clearly see distant things but not so clearly perceive objects close to them. The image is created behind the retina in this scenario. Hypermetropia can be treated by wearing spectacles with a convex lens of a sufficient focal length.

Refraction of Light through a Glass Prism
A prism is a transparent optical device that refracts light and has flat, polished surfaces. There must be an angle between at least two of the flat surfaces. A ray of light is deviated twice when it enters the glass prism. The first time it enters the glass prism and the second time it exits the prism. An angle is used to split the emergent ray from the incident ray. The angle of deviation is the name given to this angle.

Atmospheric Refraction Effects
Early sunrise and late sunset: We can see the sun around 2 minutes before sunrise and 2 minutes after dusk. This is due to the apparent flattening of the sun’s disc induced by air refraction of sunlight at sunrise and dusk.

Sun Reddening at Sunrise and Sunset: Sunlight near the horizon goes through a thicker layer of air and must travel a greater distance to reach the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. As a result, much of the blue light with shorter wavelengths is scattered away by air particles, and the light that reaches our eyes has a longer wavelength, giving the sun a reddish colour. However, light from the overhead sun at midday must travel a shorter distance, so only a small amount of blue and violet light is scattered, making the sun appear white.

Important diagrams of chemistry
Lewis structures (also known as “Lewis dot structures”) are two-dimensional graphical formulas that depict atom connection and lone pair or unpaired electrons. This is the most common notation for tiny molecules. Each line represents a single bond’s two electrons. Double and triple bonds are represented by two or three parallel lines between pairs of atoms, respectively

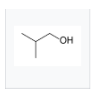
Skeletal formulas
For more complicated organic molecules, skeletal formulas are the conventional nomenclature. The carbon atoms are implied to be situated at the vertices (corners) and ends of line segments rather than being marked with the atomic symbol C in this sort of diagram, which was initially employed by organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé von Stradonitz[1]. The number of hydrogen atoms connected to carbon atoms is not mentioned; each carbon atom is assumed to have enough hydrogen atoms to form four bonds.
Skeletal diagram of isobutanol
Conclusion
Creating physics diagrams for classroom use might be a time-consuming undertaking if you’re a teacher. To help with this, I made a series of diagrams that are widely used in physics classes. It’s also helpful to have general diagrams since you can add problem-specific information like labels and force vectors to them. The physics diagrams are categorised according to which branch of physics they belong to. Physics diagrams are extremely useful for grasping the fundamental concepts of physics. We can visualise any issue and remember the concept for a long period if we study physics diagrams properly. To grasp a notion in physics, we use a free body diagram, or FBD. FBD diagrams are primarily graphical representations of concepts that aid in visualisation, such as applied force and body movement.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out