A heat engine does work by using energy provided in the form of heat and then exhausting the heat that cannot be used for work. The study of the interactions between heat and work is known as thermodynamics. The operation of a heat engine is constrained by the first and second laws of thermodynamics. The first law applies energy conservation to the system, while the second restricts the machine’s possible efficiency and defines the direction of energy flow.
PV diagrams (Pressure-Volume) diagrams are a common visualization tool used to examine heat engines. Because gas is commonly used as a working ingredient in engines, the ideal gas law connects the PV diagram to the temperature, allowing the three fundamental state variables for the gas to be tracked throughout the engine cycle. Because labor is only done when the volume of the gas changes, the diagram depicts the work performed. Since internal energy is limited. The PV diagram, coupled with the temperatures obtained from the ideal gas law, determines the changes in the internal energy of the gas, allowing the first law of thermodynamics to be used to compute the amount of heat added. In conclusion, the PV diagram serves as a foundation for analyzing any heat engine that uses a gas as a working ingredient.
A closed loop PV diagram will be used for a cyclic heat engine. The amount of work done throughout a cycle is represented by the area inside the loop. By comparing an engine cycle’s PV diagram to that of a Carnot cycle, the most efficient type of heat engine cycle, one can get a sense of its relative efficiency.
Heat Engine Diagram
A heat engine does work by using energy provided in the form of heat and then exhausting the heat that cannot be used for work. The study of the interactions between heat and work is known as thermodynamics. The operation of a heat engine is constrained by the first and second laws of thermodynamics. The first law applies energy conservation to the system, while the second restricts the machine’s possible efficiency and defines the direction of energy flow.
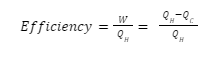
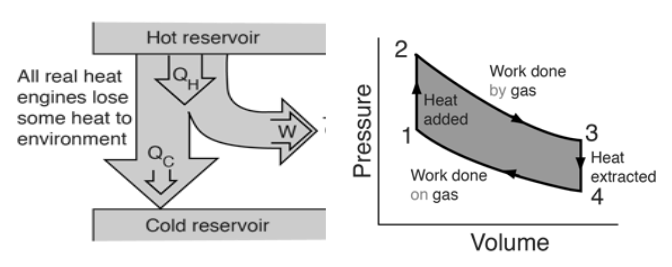
Energy Reservoir Model
The energy reservoir model is one of the most common ways to depict a heat engine. The engine absorbs energy from a hot reservoir and utilizes some of it to accomplish work, but is forced to exhaust some of it to a cool reservoir by the second law of thermodynamics. The hot reservoir in an automotive engine is the burning fuel, whereas the cold reservoir is the atmosphere into which the combustion products are released.
Efficiency
Although the efficiency expression is broad, the highest efficiency is confined to the Carnot cycle. The thermal bottleneck is a term used to describe this problem.
Heat Engine Uses
1.Earth’s heat engine
When transporting heat over the globe, Earth’s atmosphere and hydrosphere are coupled systems that constantly even out solar heating imbalances through evaporation of surface water, convection, rainfall, winds, and ocean circulation.
2.Phase-change cycles
The operating fluids in these cycles and engines are gases and liquids. The engine changes the working fluid from a gas to a liquid, a liquid to a gas, or both, and generates work by expanding or compressing the fluid.
- Cycle of Rankine (classical steam engine)
- Cycle of regeneration (steam engine more efficient than Rankine cycle)
- Rankine cycle (organic) (Coolant changing phase in temperature ranges of ice and hot liquid water)
- Cycle of vapor to liquid
3.Gas-only cycles
- The operating fluid in these cycles and engines is always a gas.
- Cycle of Carnot (Carnot heat engine)
- Stirling cycle (Caloric Ship John Ericsson) Ericsson cycle (Caloric Ship John Ericsson)
Conclusion
A heat engine is a sort of engine (similar to a car’s motor) that uses heat to produce macroscopic motion. Friction converts mechanical energy (the action of our hands) into heat energy when people rub their hands together (the hands get warmer). Heat engines, on the other hand, take the energy that comes from being warm (in comparison to the surroundings) and convert it into motion. A generator is frequently used to convert this motion into electricity.
Heat engines provide nearly all of the energy used in transportation and electricity generation. The thermal energy of hot items, including gases, can be converted into something useful. Heat engines transfer energy from a hot to a cool location and convert some of it to mechanical energy to work, heat engines require a temperature difference.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






