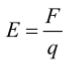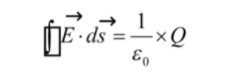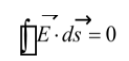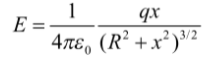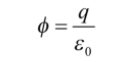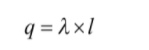According to Gauss Law, total electric flux outside a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed which is separated by the permittivity. The electric flux is the product of electric field and area of the surface which is projected in a plane and normal to the field.
Electric Field
The electric field is defined in mathematical terms as a vector field which can be connected with each point in space. At that point the force per unit charge is exerted on a positive test charge which is at rest.
The electric field is given as
Here,
E = electric field
F = force
q = charge
Unit:
Gaussian Surface
A closed surface in a 3D Space whose flux of a vector field is determined which may be the magnetic field or electric field or gravitational field is called the Gaussian surface.
Gauss Law
According to the Gauss Law total electric flux outside the closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by that surface divided by the permittivity (). The electric flux in an area is the product of electric field and the area of the surface perpendicular to the field.
Total flux associated with the surface is 1/ ε0 times the total charge enclosed by the closed surface.
Hence, it is given as
Electric Field using Gauss Law
The electrostatic field/electric field can be determined by following these steps.
- Firstly, we need to find the spatial symmetry (spherical, planar, cylindrical) of distributed charge.
- Then, we have to determine a gaussian symmetry which is similar to the symmetry of spatial arrangement.
- Determine integral along with the gaussian surface and then define flux.
- Determine the charge which is enclosed by the Gaussian surface.
- Determine the electric field of distributed charge.
Gauss law in a Conductor
Electric field inside a conductor is always zero. As the net or total electric charge in the conductor becomes zero. Therefore, no electric flux is trapped or enclosed in the conductor.
Hence Gauss’s law within a conductor given as
Gauss Law Application
There are many applications of Gauss law.
- Electric field when a charged ring having radius R on its axis at a distance of x from the centre is given as
2. Electric field between two plates which are parallel to each other is given as
Here, = charge density
Electric field Due to Infinitely Long Straight Uniformly Charged wire
Electric field due to Infinitely long uniform charge will be determined easily by applying Gauss law. It is a Gauss law application. Let us consider a line charge in the form of a thin charged rod having linear charge density λ.
For determining the electric intensity at a point P at a normal distance r from the rod, we need to consider a right circular closed cylinder having radius equals to r and length is l with an infinitely long line of charge as its axis.
The magnitude of the electric field intensity at all points on the curved surface of the Gaussian surface (cylinder) is the equivalent because the distance of all points are the same from line charge.
Hence,
Curved surface area =2Πrl
Now, we know
And
And also, Gaussian surface is given as
Therefore, by combining these three equations we get
Here,
=Line Charge Density
l = length
Hence, Electric field due to Infinitely long uniform charge is
Limitations of Gauss Law
There are some limitations of Gauss law which are given here.
- One cannot determine the electric field for any conductor. Gauss’ law is only useful for some symmetrically charged conductors such as spheres, cylinders, straight wires, flat sheets, etc. to calculate electric fields.
- Gauss law is applicable when the conductors have charges inside them.
- You can use Gauss’ law to determine an electric field due to a point charge. But Gauss law is not used to determine an electric field for an electric dipole and other conductors having irregular shape. Coulomb’s law is used to find the electric field of an electric dipole.
Conclusion
The electric field is defined in mathematical terms as a vector field which can be connected with each point in space.
The electric field is given as
A closed surface in a 3D Space whose flux of a vector field is determined which may be the magnetic field or electric field or gravitational field is called the Gaussian surface.
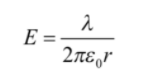
Electric field when a charged ring having radius R on it’s axis at a distance of x from the centre is given as
Electric field between two plates which are parallel to each other is given as
Here, = charge density
According to the Gauss Law total electric flux outside the closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by that surface divided by the permittivity ().
Gauss law is given as
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out