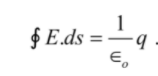Gauss Law, also known as Gauss’s flux theorem or Gauss’s theorem can be referred to as the law which explains the relation between electric charge distributions to the resulting electric field. Generally it states that the total amount of electric flux passing through any closed surface is directly proportional to the electric charge in it.
The electrical field of the surface is calculated by applying Coulomb’s law, but to calculate the distribution of the electrical field on a closed surface, the Gauss law is required. It explains the electrical charge enclosed in the closed or electrical charge present in the enclosed closed surface.
Gauss’s Law
According to Gauss’s Law “The total number of flux present in a closed surface is 10 times the total electric charge within the system.
Where q is the charge inside it.
Gauss’s law has very close mathematical similarities with various laws in other areas of physics, like Gauss’s Law for magnetism and Gauss’s Law for gravity.
In fact, any inverse-square law can be constructed in the same way as Gauss’s law: for example, Gauss’s law itself is equal to Coulomb’s inverse square law, and Gauss’s law of gravity is actually equal to the inverse-square of Newton’s law of gravity.
The law can be expressed mathematically using vector calculus in an integrated way and also in a differential way; both are similar as they relate by the divergence theorem, also called Gauss Theorem. Each of these forms can be determined in two ways: In relation to the electric field E and total electric charge, or in terms of electrical displacement field D and the free electric charge.
Gauss’s Theorem
According to Gauss’s Theorem “The net flux through a closed surface is directly proportional to the total charge in the volume enclosed by the closed surface.
It is represented by:
![]()
In other words we can say that the gauss theorem deals with the flow of electrical field lines to charges within the enclosed surface. In the case if there is no charges enclosed to the surface then the total electric flux remains zero.
Hence from this we give the conclusion that the total number of electric field lines entering the surface is equal to the total number of electric field lines leaving the surface.
Application of Gauss’s Law
Gauss’s law can be used to solve complex electrostatic problems involving unique symmetry such as cylindrical, spherical or planar symmetry.
It is also useful for calculating the electric field which is quite complex and involves tough integration. Gauss law can be used to simplify the calculation of the electrical field.
Gauss’s Law is applied in the following Manner:
- Choose Such a Gaussian surface, so that the calculation of the electric field becomes easy
- Use symmetry to make problems easier
- Remember, that the Gaussian surface does not have to be in the line with the real surface, that is, either inside or outside the Gaussian area
Conclusion
In physics and electromagnetism, Gauss’s law, also known as Gauss’s flux theorem, is a law relating to the distribution of electric charge in the resulting electric field. In its most basic form, it states that the flux of the electric field out of a closed surface is proportional to the electric charge enclosed by the surface regardless of how that charge is distributed.
Even by the law alone is not sufficient to determine the electric field across a surface enclosing any charge distribution, it is possible in cases where symmetry mandates uniformly of the field.
Gauss’s law can be applied in differential form, which states that the divergence of the electric field is proportional to the density of the charge.so in this article we have learnt about the Gauss law and its application with its various properties.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out