The attribute of inertia in a body is its ability to remain at rest or in motion until it is acted on by an external force. The inertial frame of reference takes this into account. Unless displaced by an external force, everyone examined in an inertial frame of reference tends to maintain their rest or motion posture. As a result, an inertial frame of reference might be fixed or moving at a constant speed. An automobile at a standstill or a bus moving at a steady speed are examples of inertial frames of reference.
The term “non-inertial frame of reference” refers to a frame of reference that is speeding. In a non-inertial frame of reference, a body does not appear to obey the laws of inertia. In this case, Newton’s first law of motion is no longer applicable. The acceleration of a non-inertial frame is measured in terms of an inertial reference frame. When a car is going at a certain speed, for example, it is said to be in a non-inertial frame of reference.
Frames of reference
We’ve talked about velocity, acceleration, and displacement. To measure all of the above-mentioned metrics in an actual use case scenario, all of these figures, however, require a frame of reference against which they may be tested.
In physics, a frame of reference consists of an abstract coordinate system and a set of physical reference points that later define the coordinate system and standardise measurements inside it.
Consider the following diagram:
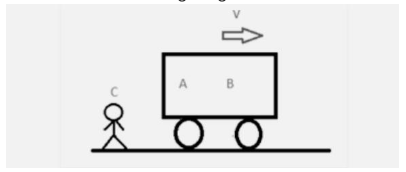
If we ask A what B’s velocity is, he’ll tell us it’s at rest. If we ask C the same question, he will tell us that B is moving at a velocity of V in the positive X direction. So, before stating the velocity, we must first describe which frame we are in, or, to put it another way, we must establish a frame of reference.
Frames of reference can be divided into two categories. The following is a list of them:
1.Inertial Reference Frame
The term “inertial frame of reference” refers to a frame of reference in which Newton’s law holds true. That is, if no external force occurs on an object, it will remain at rest or move in a consistent manner. If we assume that a body is preserved on the earth’s surface, it is at rest for a person on earth but it is in motion for a person on the moon. A reference frame that is considered to represent the inertial frame of reference is referred to as an inertial frame. According to a larger definition, an inertial frame is at rest or moves at a constant velocity with regard to our imagined inertial reference frame.
2.Non-Inertial Frame of Reference (NIFR)
A non-inertial frame of reference is one that moves quicker than the inertial frame of reference. Newton’s law will not apply in certain circumstances. As a result, if the earth is an inertial reference frame, the moon is a non-inertial reference frame because it moves faster than the earth. However, we’ll need to apply some weird forces called pseudo forces if we want Newton’s rule to hold true here.
A frame of reference that is neither moving nor moving at a constant speed is referred to as an “inertial frame of reference.” A non-inertial frame of reference is one that is always accelerating or going in a cyclic path.
As we consider Newton’s equations hold in this frame when the spectator is in space, a reference frame linked to the earth is definitely an inertial frame –
- By definition, it is an inertial frame.
- As we know the earth revolves around the sun, it cannot be an inertial frame.
- It is an inertial frame because Newton’s laws apply to it.
- This earth cannot be an inertial frame because it spins around its axis.
Conclusion
A frame of reference is a collection of coordinates that may be used to determine the locations and velocities of objects within it; different frames of reference move in relation to one another. This indicates that we can solve issues in any reference frame and get the same result. Frame of reference are useful because they allow us to take in a wide range of information and interpret it according to our prior experiences and ideals. In fact, a person’s Frame of Reference aids in life stability and decision-making speed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






