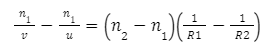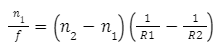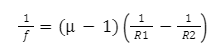The lens is a transparent medium that is bordered by two surfaces, at least one of which must be curved in order for the lens to function. When the distance between the two sides of a lens is exceedingly short, it is said to be thin. When a lens has a positive focal length, it will be converging; when the focal length is negative, it will be diverging.
Lenses are classified into two categories based on the curvature of the two optical surfaces that make up the lens. Convex and concave shapes are used.
The lens maker’s formula is the relationship between the focal length of a lens and the refractive index of its material, as well as the radii of curvature of the two surfaces on which it is constructed. Glass with a specific refractive index is used by lens manufacturers to create lenses of specific powers using glass with a specific refractive index.
Because the lens is narrow, the distances measured between the poles of the two surfaces of the lens can be assumed to be equal to the distances measured between the optical centre and the poles of the two surfaces of the lens.
Focal length and radius of curvature definition
A converging lens is used to bring parallel light rays together into a single point, while an opposing lens is used to make the refracted light appear to diverge from a single point (for a diverging lens). The point at which the lens is focused is referred to as the lens’s focal point. The focal length is defined as the distance between the optical centre and the point of interest.
Two spheres are represented by the curved surfaces of a lens. The curvature of the lens is defined by the radii of these spheres, which are measured in millimetres. The radii of the lens alter depending on the geometry of the lens.
Lens maker’s formula
To put it simply, this formula connects the focal length (f) of a lens to its refractive index and the radii of curvature of its two surfaces. The focal length of a lens is determined by the refractive index of the material used to construct the lens as well as the radius of curvature of the lens. This formula is utilised by lens manufacturers to create the desired lens, and as a result, it is referred to as the lens maker’s formula.
Sign conventions:
A “positive (+ve)” length is defined as the distance measured from the optic centre to the right-hand side.
A “negative (-ve)” length is defined as the distance measured from the optic centre to the left-hand side.
Everything is measured in terms of distance from the optic centre.
Lens maker’s formula Derivation
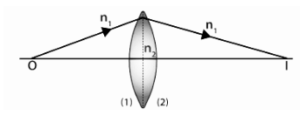
Assumptions
For the purpose of deriving the lens maker formula, the following assumptions have been made.
Consider the narrow lens depicted in the image above, which has two refracting surfaces with radii of curvature R1 and R2, which are different from one another.
Given that the refractive indices of the surrounding medium and the lens material are n1 and n2, the following equation can be used:
Derivation
The next section describes the comprehensive derivation of the lens maker formula. With the help of a refraction formula applied to a single spherical surface, we may say that
For the first surface,
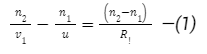
for the second surface
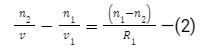
by adding or comparing (1) and (2), we have
When u = ∞ and v = f, we can say that
Then we will get,
Where μ is the refractive index.
CONCLUSION
Real lenses have a finite thickness between their two surfaces of curvature since they are made of two surfaces of curvature. The optical power of an ideal thin lens with two surfaces of equal curvature will be zero for a perfect thin lens with two surfaces of equal curvature. Light will not converge or diverge as a result of this property. A thick lens is a lens that has a significant amount of thickness that is not trivial.
As a result of this, we can deduce that a convex lens does not necessarily have to be converging, and that a concave lens does not necessarily have to be diverging. Every lens has a unique value that may be calculated by applying the lens manufacturer’s formula to the lens.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out