When one mole or Avogadro’s number of electrons is charged, the Faraday constant represents the amount of electric charge that is carried by that mole. It is a fundamental constant in chemistry, physics and electronics and it is commonly represented by the italic uppercase letter F in these fields of study. Coulombs per mole (C/mol) is the unit of measurement.
Faraday’s constant can be calculated by dividing the Avogadro constant, which is the number of electrons per mole, by the number of electrons per coulomb, which is the number of electrons per coulomb.
Therefore:
F = (6.02 x 1023 ) / (6.24 x 1018 )
= 96485.3329 C/mol
About Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who made significant contributions to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. He was born in London and died in London. His most important discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis, among other things.
Faraday was an excellent experimentalist who communicated his ideas in a clear and simple manner; his mathematical abilities, on the other hand, were limited to the simplest algebra and did not extend as far as trigonometry. Taking the work of Faraday and others and distilling it into a set of equations, James Clerk Maxwell laid the groundwork for all modern theories of electromagnetic phenomena that are still in use today. Avogadro’s number of electrons, also known as Faraday’s constant, is the amount of electric charge carried by one mole (or Avogadro’s number of electrons) of electrons.
Faraday Constant Formula
This constant can be expressed in terms of two other physical constants, which is,
F = eNA
Where,
e is the charge of the electron in coulombs e = 1.60217662×10−19 C
NA is the Avogadro constant. NA = 6.022141×1023 mol−1.
Calculation of Faraday constant
It is the charge of one mole of electrons that is denoted by the Faraday constant in physical chemistry, which is represented by the symbol F and sometimes stylized as F. In electrochemistry, it can be thought of as a conversion factor between the mole (a unit of measurement used in chemistry) and the coulomb (a unit of measurement used in physics and in practical electrical measurements), and it is particularly useful in electrochemistry. It was given this name in honour of Michael Faraday and its currently accepted value is
F = 96485.33212… C⋅mol−1.
Considering that 1 mol electrons is equal to 6.022*1023 electrons (Avogadro’s number) and that 1 coulomb is equal to the (negative) charge of 6.241*1018 electrons, the Faraday constant can be calculated as the quotient of these two numbers:
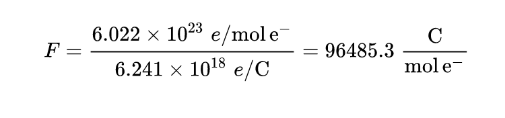
F was first calculated by weighing the amount of silver deposited in an electrochemical reaction during which a measured current was passed for a measured time and applying Faraday’s law of electrolysis to the resultant weight.
Due to the 2019 redefinition of the International System of Units (SI), which introduced precisely defined values for the elementary charge and the mole, the Faraday constant has been precisely defined.
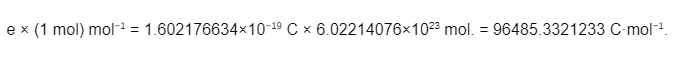
Various other common units
- 96.485 kJ per volt–gram-equivalent
- 23.061 kcal per volt–gram-equivalent
- 26.801 A·h/mol
The Faraday unit of charge is defined as
The “faraday” which is a unit of electrical charge, is closely related to Faraday’s constant. Though much less common than the coulomb, it is still occasionally employed in electrochemistry. 96485.33212… C. One faraday of charge is equal to the magnitude of the charge carried by one mole of electrons, which is equal to 96485.33212… C.
The Faraday constant F, when expressed in faradays, equals “1 faraday of charge per mole of matter.”
Not to be confused with the farad, which is a completely unrelated unit of capacitance (1 farad = 1 coulomb / 1 volt), this faraday unit is used to measure resistance.
In addition, the Faraday constant provides the amount of energy, measured in J mol-1, that is equivalent to one electron volt.
Applications
The electrolysis process is one of the most common applications of the Faraday constant. The amount of charge in coulombs divided by the Faraday constant gives the amount of oxidised elements in moles when the charge is expressed in coulombs.
Conclusion
Faraday’s constant is, in essence, the charge that one mole of electrons can carry in one second. Despite the fact that it is less commonly used, it is primarily employed in the field of electrochemistry. This is a conversion factor between the units of a mole and a coulomb of energy. This number represents the amount of electric charge carried by a mole of electrons, also known as Avogadro’s number. It is a fundamental constant in chemistry, physics and electronics and it is commonly represented by the italic uppercase letter F in these fields of study. Coulombs per mole (C/mol) is the unit of measurement. Faraday’s constant can be calculated by dividing the Avogadro constant, which is the number of electrons per mole, by the number of electrons per coulomb, which is the number of electrons per coulomb.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






