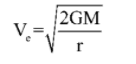Why doesn’t a ball go through the atmosphere and into space when you throw it into the air? This is due to the gravitational force pulling it back down. So, how does a rocket go into space? It can fly into space since it is moving at such a high velocity. This is referred to as the escape velocity. The escape velocity of celestial bodies such as planets and their natural satellites (the moon for us) is the lowest velocity that an object must accomplish in order to leave the celestial body’s gravitational sphere of influence (pull, push, or attraction). The total of the system’s gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy will be equal to zero at this velocity.
What is Escape Velocity?
In astronomy and space research, escape velocity is the velocity required for a body to escape from a gravitational centre of attraction without additional acceleration. The escape velocity decreases with altitude and equals the square root of two times the velocity required to maintain a circular orbit at the same height. If air resistance were ignored at the Earth’s surface, escape velocity would be around 11.2 kilometers per second. At its surface, the velocity of escape from the less massive Moon is around 2.4 kilometers per second. A planet (or satellite) cannot sustain an atmosphere for long if its escape velocity is close to the average velocity of the gas molecules that make up the atmosphere.
For example, if a spacecraft escapes the earth’s surface, it must travel at a speed of 7 miles per second, or around 25,000 miles per hour, without ever falling to the earth’s surface.
Equation of escape velocity
The escape velocity equation is calculated by equating the kinetic energy of an object with mass m and moving at a velocity of v with the gravitational potential energy of the same object.
Where, G = gravitational constant, M = mass of the object escaped, r = distance from the center of mass
Escape Velocity of Earth
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Radius of the earth, R =6.4×106m
The escape velocity of the earth, ve = 11.2 km/s
At the surface, the earth’s escape velocity is around 11.2 km/s. This indicates that in order to escape Earth’s gravity and go to infinite space, an object’s starting velocity must be at least 11.2 km/s.
The minimal speed necessary to escape the gravitational attraction of a planet is referred to as the escape velocity.
For example, if we take the earth to be a large body, the escape velocity is the minimum velocity that an object must attain in order to overcome the earth’s gravitational field and fly to infinity without falling back.
This is determined by the object’s distance from the large body as well as the mass of the large body. It will be higher if the mass is greater. Similarly, the greater the distance, the greater the escape velocity will be.
Escape Velocity of Moon
Planets with a higher mass are more difficult to escape than planets with a lower mass. This is due to the fact that the more mass a planet has, the stronger its gravitational pull. When you view images of astronauts jumping on the Moon, it appears simple. This is due to the Moon’s substantially lower mass (and hence gravity) than the Earth’s. Now, let’s put in some values to calculate the escape velocity from the Earth’s surface. We use the mass of the Moon, which is 1.74×1022 kg, as M.
Because we are calculating the escape velocity from the surface of the Moon, we may use the radius of the Moon, which is1.74×106 m, as.
After calculation by using the formula of escape velocity, the Moon’s escape velocity is =1.68×103 m/sec
Conclusion
The invisible force is applied by the earth on every object that is on the earth and that force is known as the gravitational force. But In case if some object has to travel to space then it will have to travel at the velocity at which that can leave the earth’s atmosphere. Moreover this is applicable for other planets such as Jupiter, mercury etc and on the moon too. Although in this article you will also know about the equation of the escape velocity and by using that equation you can calculate escape velocity of any other planet. Hope this article is useful for you.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out