The wave nature of electrons has been a long-debated topic in the world of physics since it was first deduced by Max Planck in his paper Quantum Theory of Radiation (1901). In this paper, Planck proposed that light energy was emitted from atoms as discrete bundles called quanta, which were the minimum units in light emission and absorption. Later on, Albert Einstein suggested that electromagnetic waves are made up of two separate components, such as electric and magnetic waves. He proved this theory by using the photoelectric effect that showed an increase in electric current when photons strike metal surfaces due to the presence of electrons.
Wave Nature of Electron
From the beginning of time, the wave nature of electrons has been one of the most counter-intuitive concepts of physics. Einstein’s photoelectric effect, De Broglie’s hypothesis, and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle shed light on the dual nature of particles, which has resulted in current scientific understanding that all particles have a wave nature and vice versa. This behaviour has been observed not just in elementary particles but also in composite particles such as atoms and molecules.
The wave nature of electron or wave-particle duality is a fundamental feature of quantum mechanics. It simply means that subatomic particles, like electrons, are both particles and waves at certain times and places. The wave nature of an electron is seen in its wave function. Unlike macroscopic waves, which are big enough to see, electron waves exist at such a small scale that we cannot detect them directly with our senses.
De Broglie’s Hypothesis
De Broglie’s hypothesis is of great importance in understanding the wave nature of electrons. This hypothesis claims that there is uniformity in nature and if light and radiation possess both particle-like and wave-like nature, matter will exhibit the same!
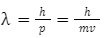
– wavelength of the particle
p – the momentum of the particle
Through de Broglie’s equation, we can get the wave theory of matter.
Electron Wave Function
In quantum mechanics, each particle has an associated wavelike quantity called a wave function that indicates where it is likely to be found or what it is likely to do next. Today, scientists are still using electron wave functions to explain how electrons move around within atoms and molecules. This makes wave functions critical for quantum chemistry calculations and quantum mechanics research in general; but also for understanding why chemical bonds form between atoms!
Schrödinger’s Equation
The concept of electron wave function was explained in 1925 for the first time with the help of Schrödinger’s equation. The Schrödinger equation is the linear partial differential equation that describes the wave function.
It is based on three things:
Classical plane-wave equation
De Broglie’s hypothesis
Conservation of energy
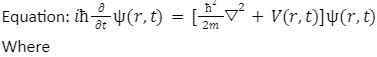
m: mass of the particle
⛛: Laplacian operator
= h/2𝝿; reduced Planck constant
E;constant equal to the energy level of the system
Properties of Wave Function
The particle’s entire quantifiable information is available.
Ψ should be continuous and have a single value
Calculating energy becomes simple when using the Schrödinger equation.
The wave function is used to create a probability distribution in three dimensions.
If a particle exists, the probability of finding it is one.
Characteristics of Electronic Waves
Listed below are some of the characteristics and properties of electronic waves:
Electronic waves propagate with the help of electric and magnetic fields that are oscillating perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation. This makes electronic waves Transverse in nature.
EM waves are a resultant of accelerated charges that induce a magnetic field perpendicular to its electric field.
Electronic waves travel at the speed of light i.e., 3 x 108 m/s and exhibit constant velocity in a vacuum.
Unlike matter waves, electronic waves do not require a medium to travel.
EM waves follow the principle of superposition.
The frequency of electronic waves remains constant irrespective of the medium, but their wavelength differs from medium to medium.
The reason for the optical effect due to electromagnetic waves is the light vector.
The electric and magnetic fields that make up an electronic wave oscillate in a phase and their magnitudes have a constant ratio.
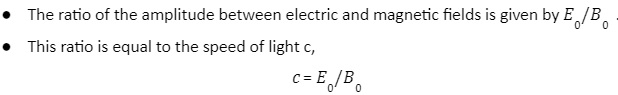
Conclusion
Understanding how electromagnetic waves work is one of several concepts that play a key role in building and using modern technology. Learning these concepts as a student gives you great insight into both how our world works, as well as learning about inventions such as electricity or wireless communication. The wave nature of electrons is said to be very important in terms of how modern electronics work. The wave-like properties allow electrons to occupy many different states in a substance at once, which is why electrons are able to flow through a conductor so easily. However, these same wave-like properties can also cause electron interference and scattering effects that are undesirable in devices such as digital computers.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




