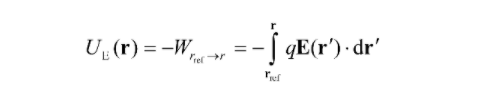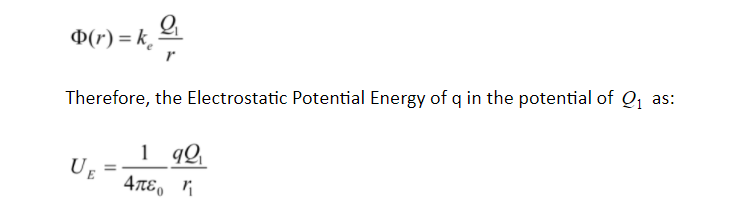Generally Electric potential energy, is potential energy (measured in joules) that obtain from conservative Coulomb force and is related with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a specified system. An item may have an electric potential energy by virtue of two key factors: Its own electric charge and its relative position to other electrically charged objects.
The term “electric potential energy” is used to describe potential energy in systems with varying degrees of electric field, while the term “electrostatic potential energy” is used to describe potential energy in systems with static or time-invariant electric fields.
Definition
Generally the electric potential energy of a system of point charges is defined as the work required to assemble this system of charges by bringing them closer together, as in the system that comes from an infinite distance.
Alternatively, the electric potential energy of any given charge or system of charge is called the net work done by an external agent in bringing the charge or a system of charge from infinite to present configuration without undergoing any acceleration.
Electrostatic potential energy, U, of one point charge q at position r in the presence of an electric field E is defined as the negative of the work W done by the electrostatic force to bring it form the reference position rref to that position r.
Mathematically, it is represented as:
Here, E is the electrostatic field.
dr is the displacement vector.
Energy Stored in a system of one point charge
The electrostatic potential energy of a system containing a single point charge is zero, as there are no other source of electrostatic force against which an external agent must perform the function of moving the point charge from infinity to its final location.
A common question arises about the interaction of the point charge with its electrostatic potential. Since this interaction does not work to charge the point itself, it does not contribute to moving the point charge itself, it does not contribute to stored energy of the system.
Energy Stored in a system of two point charges
Let us Consider a point charge, q , into its final position close to a point charge Q1. Hence the electric potential due to Q1 is:
Therefore, the Electrostatic Potential Energy of q in the potential of Q1 as:
Where r1 is the separation among the two point charges
Zero Potential
The nature of potential is that the zero point is arbitrary and can be set like the origin of a coordinate system. That doesn’t mean it is insignificant, if the zero of potential is set, then the total amount of potential is measured in relation to that of zero. One way to say this is that, it is the change in potential which has physical significance.
The zero potential (voltage) is set for easy use, but usually there is some practical or geometric concept in the choice of zero point. For a unit point charge or localized collection of charges, it is logical to set the zero point at infinity. But for an infinite line charge, that is not a reasonable option, because the local values of potential would go to infinity. In electrical circuits, ground or earth potential is generally considered as zero and everything is referenced to the earth.
Conclusion
In this article we have studied Electric potential energy. Electric potential energy is the energy required to move a charge against an electric field. You need more energy to continue moving a charge in the electric field, but also more energy to move it to a stronger electric field.
Electrical potential, or voltage, is the difference in potential energy per unit charge between two points in an electric field.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out