In classical mechanics, force, energy and potential are related to each other. A body accelerates due to the net force acting on that body. As the body moves further the kinetic energy increases and its potential energy decreases. Object possessing electric field property exerts a force on charged objects. If the charged object is positively charged, the force will be in the direction of the electric field vector at that point while if the charge is negative then the force will be in the opposite direction. The magnitude of the force is the magnitude of charge multiplied by the magnitude of the electric field vector.
Introduction To Electric Potential:
The electric potential at a point r in a static electric field E is given by the line integral
V=-c∫E.dl
Where c is an arbitrary constant path from some fixed reference point to r. The total charge of an isolated system remains constant and from the Maxwell third equation ∇×E=0 in electrostatics, we conclude that the electric field is conservative. Thus, the line integral above doesn’t depend on the particular path C chose but only on its starting and finish point. This gives an idea that electric potential V is well-defined everywhere.
The electric field in vector calculus notation is given by the negative of the gradient of the electric potential,
E=-∇V
This expression specifies how the electric field is calculated at a given point.
An electric potential can be easily understood by the concept of potential energy. Potential energy refers to the stored energy that an object has inside it or it’s the energy that every object stores inside it.
Furthermore, a charged particle in an electric field has potential energy and because of this electrostatic force can act on it. Also, it is often useful to be able to describe the potential energy on the charge per unit at a certain point or position. Moreover, this potential energy per unit charge is the electric potential.
In simple words, we can say that electric potential is the energy per unit charge that we use to describe potential energy based on the position of the object. Moreover, it resides inside the object in the form of a charge.
Electric Potential Formula:
The electric potential at a point in an electric field is the amount of work done in moving a unit positive test charge from infinity to that point against the electrostatic forces.
Electric Potential = work done / test charge
i.e. V = W /q0
Where V is the Electric potential
W is the amount of work done in moving the test charge q0 from infinity to the reference point.
q0 is the positive unit test charge.
Unit of Electric Potential
The unit of potential energy is Joules (J) and one joule is equal to 1 kgm2/s2.
The unit of charge is the coulomb (C)
The unit of electric potential in volts (v)
Therefore, by the formula of Electric Potential, we get that,
Volt = Joules/ coulomb
i.e v= J/C
Hence, the unit of Electric Potential is Joules/Coulomb (J/C) or volt (V).
The electric potential difference between two locations is one volt if it takes one joule of work to move one Coulomb of charge from one location to the other.
Derivation of electric potential:
We are going to derive the equation to calculate the electric potential at point P at a distance ‘r’ from the center. To derive this equation we have to consider a positive point charge q placed at the origin O. By definition, the electric potential at point P will be equal to the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive point charge from infinity to the point P.
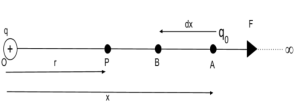
Electric potential due to a point charge.
Suppose a test charge q0 is placed at point A at distance x from O. A test charge is a charge that is used to measure the electric field strength. By Coulomb’s law, the electrostatic force acting on charge q0 and q is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. It is mathematically expressed as

Thus the electric potential due to a point charge is spherically symmetric as it depends only on the distance of the observation point from the charge and not on the direction of that point concerning the point charge. Moreover, we note that the potential at infinity is zero.
Conclusion:
The electric potential at a point in an electric field is the amount of work done in moving a unit positive test charge from infinity to that point against the electrostatic forces. The electric potential is a scalar quantity. This is a characteristic property of any point in a field.
The SI unit of the electric potential is volt(V). The electric potential at a point in an electric field is said to be 1 volt if one joule of work has to be done in moving a positive charge of 1 coulomb from infinity to that point against the electrostatic forces.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



