The analysis of systems involving vectorial electric fields increases in complexity with an increase in the number of charges involved, mainly due to the addition of multiple vectors. Energy concepts circumvent that problem as they deal with scalars only. Scalar addition is much easier to implement. In addition, for systems involving continuous charge distribution, the integration and differentiation are straightforward compared to vectorial integration and differentiation. An added advantage is that energy analysis can be converted to conventional vector analysis with little effort.
Continue reading for detailed notes on the electric potential for multiple charges.
Potential of a Single Charge
The potential V for a single charge is defined as the work done in bringing a unit charge from infinity to a distance r which comes out to be

The equipotential (i.e., the loci of points with the same potential) for a single point charge are concentric spherical surfaces.
Superposition Principle
The potential of two point charges at a certain point is the sum of the potential of charges taken one at a time. This is the superposition principle for the potential of charged particles.
If V(q) is the potential due to charge q and V(q’) is the potential due to charge q’, then according to the superposition principle, potential V(q+q’) due to charges q and q’ will be
V(q+q’) = V(q)+(q’)
If all potentials are being calculated with an identical reference point.
The superposition principle cannot be proved. It is experimentally verified.
There is nothing obvious about the superposition principle. For example, squares of real numbers do not follow the superposition principle, (a+b)² , where a and b are real numbers.
Potential of Multiple Charges
The superposition principles simplify our task of finding the electric potential for multiple charges.
The potential Vnet of multiple charges q1 ,q2 ,q3 ,q4 ,…,qn at distances respectively r1 ,r2 ,r3 ,r4 ,…,rn can be summed as

Please note that:
- Distances r1,r2,r3,r4,…, rn are measured in the same inertial frame of reference.
- This is a scalar addition, and directions play no role in calculating the potential.
- Potential due to a positive charge is added while potential due to a negative charge is subtracted, i.e., we include the sign of the charge during the summation of potentials.
Potential of a Dipole
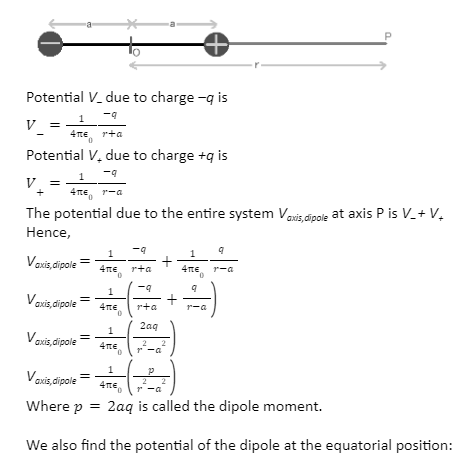
In this section, we find out the potential due to equal but opposite charges q and –q that are separated at a distance of 2a from each other. This system is called a dipole (di = two poles of opposite charges).
We find the potential at axis point P at a distance r from the centre of the dipole.

Potential Due to Continuous Charge Distribution
The summation of potential can be easily modified to an integral for continuous charge distributions as:
Charge distributions can be linear on a surface or solid. Accordingly, we represent:
- Linear charge distribution λ as charge per unit distance
=dq ⁄ dx
where q represents charge and x represents distance. The potential for a linear charge distribution is

We know that charge distribution is uniform. Hence, the linear charge density can be found by dividing the net charge by the distance of the rod.
λ=Q ⁄ L

- Surface charge distribution as charge per unit area
=dq ⁄ dA
where q represents charge and A represents the area. The potential for a surface charge distribution is then

Conclusion
We found out that the superposition principle vastly simplifies the electric potential for multiple charges, one of the most important charge distributions. The dipole’s potential at equatorial and axial positions is also discussed. Furthermore, these notes on the electric potential for multiple charges can help you find the potential of continuous charge systems.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






