To learn about electric potential derivation, we need to know the electrostatic potential. Potential is the amount of work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Line integration of electric field
Line integration of an electric field is the amount of work done to move unit positive charge along the line from one point to another inside the electric field.
∫E.DL= Wab/q。
where E the is electric field, and Wab is work done with respect to a and b
E = q/4πЄ。r2
here, q is charge, and r is the distance covered by the charge.
The small amount of work done to move the charge can be represented as:
dw = F.DL
here, F is force
= q。E.DL
= q。E.DLcosθ
dw = q。(q/4πЄ。r2)dr
Wab/q。= ∫(q/4πЄ。r2)dr (having limits from ra to rb)
= -q/4πЄ。(1/rb-1/ra )
∫E.DL= q/4πЄ。(1/ra-1/rb)
Line integration of electric fields depends only on the initial and final position of the charge and not on the path of the charge. This shows that electric force is conservative.
The line integration of electric fields over a closed path is always equal to zero.
Negative line integration gives a potential difference between two points.
Potential difference between two points
The electric potential difference between any two points is the amount of work done to move a unit positive charge without accelerating from one point to another against the direction of electric force.
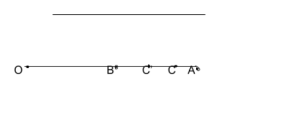
Where OB = rb , OA = ra , OC = r
VB – VA = Wab/q。
The small amount of work done in order to move unit positive charge from C to C’:
Dw = F.DL
= – q。E.DL
= -q。E.DLcosθ
= -q。E.DLcos180
Dw = q。E.DL
[because DL is in the direction of dr]
Therefore, Dw = -( qq。/4πЄ。r2)dr
Wab = ∫ -( qq。/4πЄ。r2)dr (limits are from ra to rb)
Wab = ( qq。/4πЄ。)(1/rb-1/ra)
Wab/q。= q/4πЄ。(1/rb-1/ra)
VB – VA = q/4πЄ。(1/rb-1/ra)
units of potential difference are J/C
Electric potential derivation
Potential at any point is the amount of work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Dw = F.DL
= – q。E.DL
= -q。E.DLcosθ
Dw = q。E.DL
Dw = -( qq。/4πЄ。r2)dr
W∞b = ∫ -( qq。/4πЄ。r2)dr (limits are from ∞ to rb)
W∞b = ( qq。/4πЄ。)(1/rb-1/r∞)
W∞b /q。= q/4πЄ。(1/rb)
therefore,VB = q/4πЄ。(1/rb)
Electric fields as a gradient of potential
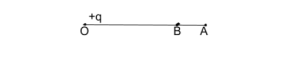
The minimum amount of work done to move a unit positive charge from A to B can be represented:
V + dV – V = Dw/q。
dV = Dw/q。
Dw = F.DL
= – q。E.DL
= -q。E.DLcos180
Dw = q。E.DL
Dw = –q。E.dr
dV =- q。E.dr/q。
dV = – Edr
E = -dV/dr
Here, the negative sign shows that the direction of the electric field is the direction in which the potential decreases with length.
Electric potential derivation due to point charge is V = q/4πЄ。r.
Electric potential derivation due to a hollow or solid conducting sphere or a solid insulating sphere (outside or on the surface) is V = q/4πЄ。R.
Electric potential derivation inside the hollow or solid conducting sphere where potential is the same on each and every point is V = 0.
Electric potential derivation at the centre of the insulating charged sphere is V = 3/2(q/4πЄ。R).
Electric potential derivation when r < R is V = (q/4πЄ。R)(3/2 – r2/2R2).
Electric potential derivation on the equatorial line of electric dipole
Vc = Va + Vb
here, Vc , Va and Vb are potential along a,b and c
Va = (1/4πЄ。)(-q/(a2+r2)½
Vb = (1/4πЄ。)( q/(a2 + r2)½
Therefore, Vc = 0
The potential on the equatorial line of an electric dipole is always zero.
Electric potential derivation due to electric dipole on its axial line
Va = (1/4πЄ。)(-q/r+a)
Vb = (1/4πЄ。)(q/r-a)
Vc = Va + Vb
= (1/4πЄ。)(q2a/r2-a2)
Vc = (1/4πЄ。)(P/r2 – a2)
Electric potential derivation due to electric dipole at any point which makes an angle θ with the dipole moment
Va = – (1/4πЄ。)(q/r + acosθ)
Vb = (1/4πЄ。)(q/r – acosθ)
Vc = Va + Vb
Vc = (1/4πЄ。)(q)(1/r – acosθ – 1/r + acosθ)
Vc = (1/4πЄ。)(q)(2acosθ/r2 – a2 cos2θ)
Vc = (1/4πЄ。)(q)(Pcosθ/r2 – a2 cos2θ)
Electric potential derivation due to circular loop of charge (axial line)
The electric potential at any point outside the loop
Vp = (1/4πЄ。)(Q/(x2 + a2))
here, Vp is potential at point p.
At centre
Vo = (1/4πЄ。)(Q/a)
here, Vo is potential at the centre.
Equipotential surface
On an equipotential surface, there is no potential difference between any two points.
Properties of an equipotential surface are:
No work is required to move a charge from one point to another on the equipotential surface.
The electric field is always perpendicular to the equipotential surface.
Equipotential surfaces give the direction of the electric field. The negative sign shows that the direction of the electric field is the direction in which the potential decreases with distance.
An equipotential surface gives the strength of the electric field. For a change in potential, equipotential surfaces are closer where the electric field is strong.
No two equipotential surfaces intersect each other because if they intersect, we will have two different electric potentials in the common area, which is not possible. If two equipotential surfaces intersect, then there will be two different directions of the electric field at the point of intersection, which is not possible.
An equipotential surface for a uniform electric field can be derived like this:
Equipotential surfaces will also be plane sheets parallel to each other.
E = dV/dr
If E is constant, then,
dV is directly proportional to dr so,
D1 = D2
Equipotential surfaces for the point charge are spherical.
E = dV/dr
If dV is constant, then,
E is inversely proportional to dr so,
D3>D2>D1
Electric potential derivation energy of a system of charges
It is the amount of work done to bring different charges from infinity to their respective point. V = W/q
Therefore, electric potential derivation energy for n charges is,
U = (1/4πЄ。)(½)(Σi =1Σj =1 (qi*qj/rij)
Conclusion
Electric potential derivation at any point is the amount of work done to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to that point. The potential difference between any two points is the amount of work done to move a unit positive charge without accelerating from one point to another against the direction of the electric field.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






