Magnetic permeability is a constant that defines the magnetic property of that material. Like mass, it is also one of the most fundamental properties. The value of magnetic property tells how much magnetic intensity is required to magnetise that object. In simpler words, we can say that it is the measurement of the number of magnetic field lines an object allows to enter. The more the value of magnetic permeability will be, the more that material will tend to enable magnetic field lines to pass through it.
Magnetic Permeability
Magnetic permeability aids in measuring a material’s resistance to the magnetic field. In other words, it is the measurement of the degree to which the applied magnetic field can potentially penetrate a material.
The magnetic conductivity will be higher if a material has more extensive magnetic permeability.
The magnetic permeability helps the magnetic force of lines pass through a substance.
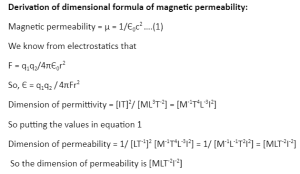
Derivation of Dimensional Formula of Magnetic Permeability
What is Permeability?
Permeability is the ability of any material to attract magnetic field lines to it. An object with a higher value of permeability can attract more magnetic field lines, and as a result, it has a higher tendency of magnetisation.
Magnetic Permeability Formula
The formula for Magnetic Permeability formula is given as:
Magnetic Permeability (μ) = B/H It is measured in Henries per metre (h/m) or newtons per ampere square.
Types of Magnetic Permeability
Permeability of Free Space
- It is also called the ‘permeability of vacuum or air’ and is represented by: μ0=B0/H
- It is the ratio of magnetic intensity in a vacuum and magnetising field.
Permeability of Medium
- It is the ratio of magnetic intensity in the medium to that of the magnetic field.
- It is represented by μ = B/H
Relative Permeability
- It is a dimensionless quantity
- It is the ratio between two quantities having the same units; therefore, the relative permeability has technically no unit. However, the Relative permeability of free space is always 1.
- It is represented with μr= μ/μm
Dimensional Analysis
Physical quantities are related to the dimensions of the measurement units used to define them. This helps us perform mathematical calculations that are easier, more precise, and quicker. In other words, it is the study of dimensional formulae. It is the technique used to manipulate dimensional formulae.
Dimensional Formula Dimensional Equation
The dimensional formula depicts the dependency of physical quantity with the fundamental physical amount and the powers.
Example
Let’s take the formula of speed:
Speed = Distance / Time
The distance can be written in length [L]
Time can be written as [T]
The dimensional formula would be [ M0 L1 T-1]
Hence, we can conclude that the speed is dependent on only length and time, not mass.
Applications of Dimensional Analysis
It determines the dimensional consistency, homogeneity, and accuracy of the mathematical expressions.
Limitations of the Dimensional Equation
- The principle of homogeneity of dimensions cannot be used for trigonometric and exponential expressions. The derivation is more complex and complicated.
- The comparing terms or factors are less.
- The correctness of the physical expressions depends only on dimensional equality.
- It is majorly used in the case of dimensional constants. We are not able to find the value of the dimensionless constant.
Applications of Magnetic Permeability
Magnetic materials constitute key pieces in technology applications for industries, such as:
- Generation, distribution and conversion of energy
- Storage and retrieval of information
- Media and telecommunications
- Magnetic Compasses
- Electric Generators
- Magnetic Tape
- Characterisation of magnetic materials
- Relation between Magnetic Permeability and Magnetic Susceptibility
The relation is established as follows
Taking relevant equations for the relationship to form.

Conclusion
In these notes of the Dimensional Formula of Permeability, we learnt how to deduce the dimensional formula of permeability and some basic concepts. These concepts are essential in figuring out the magnetic properties of different materials. Based on these, we determine the diamagnetic, ferromagnetic and paramagnetic properties. The magnetic permeability values are also necessary to decide on the hysteresis curve of different materials.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






