Impedance can be defined as the amount of resistance a component offers in a circuit at an exact frequency, where the resistance is not dependent on the frequency of the component. Here lies the main difference between impedance and resistance – impedance varies with frequency change. Capacitors are devices that show high impedance on low frequencies and low impedance on high frequencies. Inductors are the exact opposite of this which show low impedance on low frequencies and vice versa. Impedance has the same unit as resistance, which is ohm.
Impedance
An LCR series circuit is a circuit that contains resistance, capacitance and inductance in a series across an alternating current. This article will focus on in-depth reactance, impedance and resonance. We will also learn about the LCR series circuit analysis.
Impedance is a property that opposes the flow of electrons in an electrical circuit. It is a combination of both reactance and resistance. It is represented as Z and is measured in ohm.
Phasor term of impedance
Z = R + jX
Impedance in LCR Circuit
The combined opposition of both resistance and reactance is called impedance. It is denoted by Z. Impedance cannot be calculated by adding resistance and reactance. As it is an AC circuit, the R, C, L will step in and reach maximum values simultaneously.
The larger the reactance than the resistance, the more the phase difference is near 90°. The smaller the reactance than the resistance, the more the phase difference is near 0°.
Resistance and reactance can be derived by the construction of a right-angle triangle. The magnitude of the current depends on the frequency in the LCR circuit. When Z is maximum, I will be minimum.
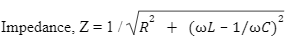
Formula of Impedance
Z = V/I
Where, V is voltage and I is electric charge
Dimensional Formula of Impedance
We know that voltage is given by work done per unit charge,
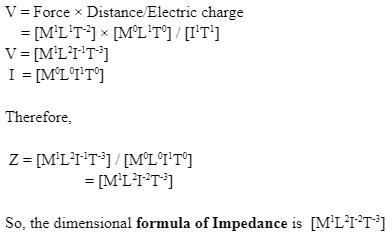
Importance of the Dimensional Formula of Impedance
- The Dimensional formula of Impedance helps us to understand the physical correctness of any equation involving force.
- It helps us to understand the relationship between different physical quantities involving heat energy.
- It helps us in converting units from one physical quantity to another.
- In any relationship, the constant dimensions can be found using this analysis.
Dimensional Formula
The dimensional formula depicts the dependency of physical quantity with fundamental physical quantity, along with the powers.
For example,
Let us take the formula of speed:
Speed = Distance / Time
Distance can be expressed in length [L]
Time can be expressed as [T]
The dimensional formula would be [ M0 L1 T-1]
Hence, we can conclude that speed is dependent only on length and time and not on mass.
Dimensional Equation
The physical quantity is equated with the dimensional formula to get the dimensional equation.
For example,
Velocity = [ M0 L1 T-1]
Here, velocity is the physical quantity, which is equated with the dimensional formula.
Conclusion
This article briefly acts as the formula notes on impedance, its dimensional formula and how it is different from resistance. A simple example, which can explain the concept of impedance in practical terms, is when a school dance troop cannot participate in a competition because they cannot afford the cost of travel to go to another city. Impedance is used to maintain the current flow in a circuit. So, it plays an important role in circuit theory. It is a property that opposes the flow of electrons in an electrical circuit. It is measured in ohm.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



