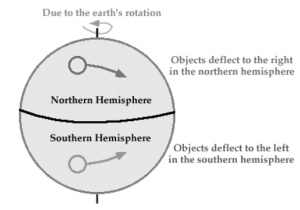
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.The Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on moving objects in a frame of reference that rotates with regard to an inertial frame in physics. The force applies to the left of the object’s motion in a reference frame with a clockwise rotation. The force acts to the right in ones that rotate anticlockwise (or counterclockwise). The Coriolis effect is the resulting deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force.
In most elementary textbooks, we are taught that centrifugal force does not exist. When a satellite orbits the Earth, it is not held in balance by two equal and opposing forces: gravity acting towards the Earth and centrifugal force acting outwards. The satellite is actually accelerating (centripetal acceleration), according to the theory; there is only one force, which is equal to the mass times the centripetal acceleration.
Yet, when we drive too fast around a corner and are hurled away from our path’s centre of curvature, the centrifugal force surely feels real enough, and we can solve problems involving rotating coordinate systems as if centrifugal force “truly” existed.
Coriolis Force origin
The motion of an object in an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference is described by Newton’s equations of motion. The Coriolis and centrifugal accelerations occur when Newton’s laws are applied to a rotating frame of reference. When applied to mass objects, the relative forces are proportional to the mass of the object. The Coriolis force has a magnitude proportional to the rotation rate, while the centrifugal force has a magnitude proportional to the square of the rotation rate.
The speed of an object determines the Coriolis force in a rotating frame and operates in a direction perpendicular to two quantities: the rotating frame’s angular velocity relative to the inertial frame and the body’s velocity related to the rotating frame (more precisely, to the component of its velocity that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation).The centrifugal force works in a radial direction and is proportional to the body’s distance from the rotating frame’s axis. Inertial forces, fake forces, or pseudo forces are the names given to these additional forces. Newton’s equations of motion can be applied to the rotating system as if it were an inertial system by introducing these fictional forces to a rotating frame of reference; these forces are correction factors that are not required in a non-rotating system.
Coriolis Force derivation pdf
Initially, the Coriolis force
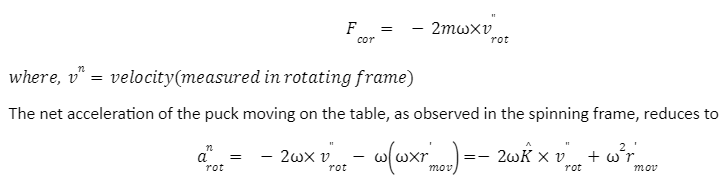
depicts the trajectory of a hockey puck in a rotating reference frame when no external forces are present, that is, when the puck goes in a straight line with constant velocity in the beginning frame.
Conclusion
The Coriolis force accelerates the puck to the right in the rotating reference frame, resulting in spiral trajectories. The apparent convoluted trajectories are due to the observer being in the rotating frame, which causes the moving puck’s straight inertial-frame trajectories to spiral in the rotating frame.
The Coriolis force is what causes winds in the northern hemisphere to circulate in an anticlockwise manner around low-pressure areas. Many activities on Earth, such as ballet dancing, ice skating, acrobatics, nuclear and molecular rotation, and missile motion, are affected by it.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out