Charging by Contact
Charging by contact is also known as charging by conduction. It is a method of charging. Any object will be charged only if there is a net excess or lack of electrons. This can be done in many ways other than charging by contact, such as charging by friction or charging by induction.
In this method of charging, a charged object comes in contact with an uncharged object and makes the latter charged.
In our everyday life, we use the word, “charging”, like nobody’s business – we’re charging our phones, iPads or computers. It actually doesn’t mean that we are taking a bunch of negative or positive charges and putting them on our phone. Something different is going on in reality. It does definitely involve some positive and negative charges though, but in a different way.
Origin of Electric Charge
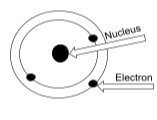
It is known that all matter is made up of atoms and molecules, the basic unit being an atom. We also know that every atom has a nucleus at its centre around which negatively charged electrons revolve in circular orbits. Every atom is electrically neutral, containing as many electrons as the number of protons in the nucleus. Thus these materials are electrically neutral, they do contain charges, their charges are exactly balanced.
On the basis of the charges in a given body or an object, we mainly classify them into two types:
Charged Body: If the positive and negative charges are not balanced, then there is some net charge. Thus, an object or a body is charged if it has a charge imbalance or some net charge.
Uncharged Body: Suppose a body or an object contains equal amounts of positive charge and negative charge. With such an equality or balance of charge, the object is said to be electrically neutral, i.e. it contains no net charge.
Now, the question arises: what is the cause of charging? What is the reason behind this charging and uncharging of the same object after coming in contact with another object?
What is the Cause of Charging?
All material particles in this universe have charges, but the magnitude of positive and negative charge in them is the same, thus they are electrically neutral. Just like all the atoms have the same number. of electrons and protons and thus they are neutral.
If due to some reason, for example, by rubbing one object with another, one object loses electrons, it becomes electrically positive, and the one which gains electrons becomes electrically negative. Thus, a body is charged only if it has a net profit or loss of electrons.
Let’s talk about some important properties of charges.
Properties of Charges
Charge is quantised – During the transfer of charge, only an integral number of electrons are transferred, thus, charge can exist in multiples of ‘e’.
Charge is conserved – Charge can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can be transferred from one body to another’
Charge is additive – Charge can be added algebraically.
Charge resides on the surface of the conductor – Charge rests only on the surface of the conductor because if the charge is within the conductor, then it will be repelled strongly by similar charges inside it. This is also known as Electrostatic Shielding.
Charge is invariant – It means that charge does not vary with increasing velocity as mass varies with increasing velocity.
Charging by Contact
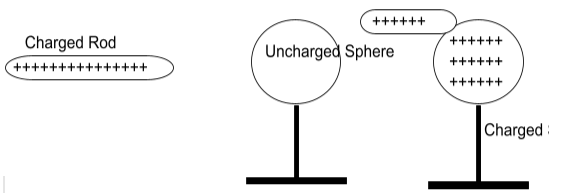
Charging by contact is really straightforward. Let’s say there is a charged balloon with -10C negative charge on it. Now take an unchanged object and make them be in contact with each other. So what do you think is going to happen? Note that there is no rubbing ,only touching, i.e. the balloon just touched it. There can be two cases, either all charges from the balloon get transferred to that uncharged object or there is only transfer of some charges.
If there are three charges remaining on a balloon, then due to conservation of charges, there must be seven charges on that object.
Key points to remember
Negative charge means excess of electrons.
Charges will be equally distributed if the shape, size and material of both conductors are the same.
Earthing is not required in the method of charging by conduction.
There is actual transfer of electrons.
Charge is a scalar quantity.
Charge cannot exist without matter.
Coulomb is the SI unit of charge.
Conclusion
It is pretty straightforward that in the method of charging by contact, when we bring any object in contact with another object, then some transfer of charges will take place simply by touching. Also, there is no need to have different types of materials. This is probably the simplest type of charging.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out