What is the Carnot cycle, and what are its stages?
When the Carnot engine works, the working substance of the engine undergoes a cycle known as the Carnot cycle. This cycle has four different stages. But before we get to know about the Carnot cycle in detail, we have to understand the second law of thermodynamics and the heat engine.
The second law of thermodynamics
Statement(I): Second law of thermodynamics states that heat can never be converted into work with 100% efficiency.
Statement(II): No engine in this world can be constructed which operates in cycles and converts all the heat from the source to work.
Statement(III): No refrigerator can be designed which operates in cycles and rejects heat from sink to source, perpetually (self- functioning).
Heat engine
The device used to convert heat energy into mechanical energy is called a heat engine. For conversion of heat into work with the help of a heat engine, the following conditions have to be met:
- A body at a higher temperature, designated ‘T1,’ should be used to extract heat. It’s known as the source.
- The working substance should be contained in the engine’s body.
- There should be a body at lower temperature ‘T₂‘ to which heat can be rejected. This is called the sink.
Working of heat engine
The schematic diagram of a heat engine is given below.
The engine derives an amount, ‘Q1‘ of heat from the source.
A part of this heat is converted into work ‘W’. The remaining heat ‘Q,’ is rejected to the sink.
Thus,
Q1 = W+Q₂
or the work done by the engine is given by
W=Q₁-Q₂
The efficiency of heat engine
The efficiency of the heat engine (n) is defined as the fraction of total heat supplied to the engine, which is converted into work.
Mathematically
Since, n = W/Q₁
Or n = Q₁-Q2/Q₁ = 1-Q2/Q₁
Carnot engine
The Carnot engine is a heat engine that uses the Carnot cycle to function. Nicolas Leonard Carnot and Sadi Carnot created the model for this engine in 1824.
It consists of different parts shown in the diagram given below:
Source: It is a reservoir of heat energy with a conducting top maintained at a constant temperature T.K. The source is so big that extraction of any amount of heat from it does not change its temperature.
Body of heat engine: It’s a cylindrical container with perfectly insulating walls and a conducting bottom. It is equipped with an airtight piston that can slide freely within the barrel. A small amount of an ideal gas is contained in the barrel.
Sink: It’s a larger body with a perfectly conducting top at a lower temperature T2. Because the sink is so huge, any heat rejected to it has no effect on the temperature of the sink.
Insulating stand: It is a stand made up of perfectly insulating material such that the barrel, when placed over it, becomes thoroughly insulated from the surroundings.
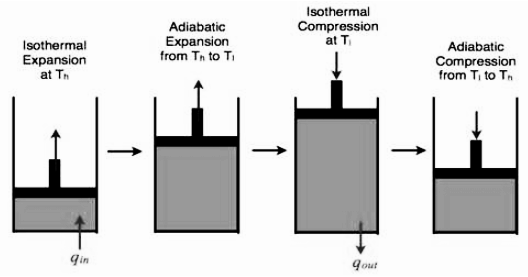
Carnot cycle and its stages
When the Carnot engine works, the working substance of the engine goes through a different cycle known as the Carnot cycle, and this cycle consists of four different stages.
1. First stage (called isothermal expansion)
In this stroke, the barrel is placed over the source. The piston is gradually pushed back as the gas expands. Fall of temperature, due to expansion, is compensated by the supply of heat from the source, and consequently, the temperature remains constant. The conditions of the gas change from A(P₁, V1) to B(P₂, V2). If W1 is the work done during this process, then heat Q₁, derived from the source is given by
W1 = -nRT1 loge(V2 / V1)
2. Second stage (called adiabatic expansion)
The barrel is removed from the source and is placed over the insulating stand. The piston is pushed back so that the gas expands adiabatically, resulting in a fall of temperature from T1 to T₂. The conditions of the gas change from B(P₂, V₂) to C(P3, V3). If W₂ is the work done in this case, then
W₂ = nCv(T2 – T1)
3. Third stage (called isothermal compression)
The barrel is placed over the sink. The piston is pushed down, thereby compressing the gas. The heat generated due to compression flows to the sink, maintaining the temperature of the barrel constant. The state of the gas changes from C(P3, V3) to D(P4, V4). If W is the work done in this process and Q is the heat rejected to the sink, then
W3 = -nRT₂ loge(V4 / V3)
4. Fourth stage (called adiabatic compression)
The barrel is placed over the insulating stand. The piston is moved down, thereby compressing the gas adiabatically till the temperature of gas increases from T₂ to T1The state of gas changes from D(P4, V4) to A(P₁, V1). If W4 is the work done in this process, then
W4 = nCv(T1 – T2)
Heat converted into work in Carnot cycle
Wcycle = W1 + W₂ + W3 + W4
⇒ – nRT1 loge(V2 / V1) + nCv(T2 – T1) – nRT₂ loge(V4 / V3) + nCv(T1 – T2)
⇒ -nR[ T1 loge(V2 / V1) + T2 loge(V4 / V3) ]
For BC, T1V2𝜸 – 1 = T2V3𝜸 – 1
For DA, T1V1𝜸 – 1 = T2V4𝜸 – 1
(V2 / V1)𝜸 – 1 = (V3 / V4)𝜸 – 1 ⇒ V2 / V1 = V3 / V4
Thus, the net work done by the engine during one cycle is equal to the area enclosed by the indicator diagram of the cycle. Analytically,
Wcycle = -nR(T1 – T2) loge(V2 / V1)
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






