The Biot Savart Law is a numerical expression that exemplifies the magnetic field produced by a stable electric flow in the specific electromagnetism of physics. It says the magnetic field in the direction of the magnitude, length, direction, as well as nearness of the electric flow. This law is basic to magnetostatics and shows an essential job connected with Coulomb’s law in electrostatics.
The Biot-Savart Law analyses the vector magnetic field dB because of an insignificant length of current. The total vector field B can be found by assimilating over the total length of all currents:
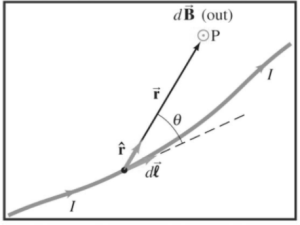
Biot-Savart’s law describes the magnetic field caused by a current-carrying segment.
At P, te magnetic field will be μ0/4 Idl sin(θ)/r2
Applications of Biot-savart’s law
There are several applications of Biot-Savart’s law in electromagnetism. Two are presented here:
a) Magnetic field due to straight wire containing current.
The magnetic induction or magnetic field at a point due to the movement of a long and straight wire: Assume PQ is a long and straight wire. A current of I amperes is flowing through it. Magnetic field at point X at r from the wire is to be determined.
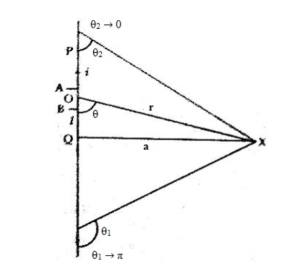
This wire is being cut into very small sections AB. Its length is dl. Distance O from the centre of that portion to point X is r, and angle ˂XOQ = θ.
As a result, the magnetic field obtained from solving the Biot-Savart Law for current element point X is,
B = μ0I / 2πa
A current-carrying wire produces a magnetic field regardless of the medium in which it is placed. However, the strength of magnetic fields caused by magnetic poles depends on the surrounding medium.
a) Magnetic field t the centre of a circular coil carrying current.
- A magnetic induction, or magnetic field, may be produced around the centre of a circular coil carrying current. For example, suppose that the flow of current through a conductor produces a magnetic field around an infinitely small area of its length. Consider the distance of a point along the wire to be r metres from the mid-point. If this distance makes an angle of ɑ with the flow of current, then by Biot-Savart’s law, the magnetic field at that point is as follows:
dB = (μ0/4π) (idl/rsub>2) sin α
The magnetic induction effect at the centre of the coil can be determined by considering a current flow of ‘i’ amperes through one turn of a circular wire radius of ‘r’ metre [Figure].
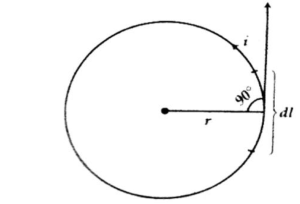
Biot-Savart’s law suggests that the magnetic field produced at the centre of the wire by a flow of current through a small portion of length “dl” of the conductor would be as follows:
dB = ( μ0idl sin α) / (4π r2) = [ μ0 (idl sin 900) / (4π r2)] = μ0 (idl/4π r2) … (1)
Here sin α equals sin 90 degree as the tangent at the midpoint of the section and the radius drawn at the midpoint are mutually perpendicular. Of course, the magnetic field will interact with the plane that contains the circular conductor.
This is because the magnetic induction produced by the whole circular wire will equal the magnetic induction produced by these small sections of the wire as they are all going in the same direction. Therefore, the total magnetic induction because of the current flowing in the whole wire is obtained by integrating the equation (1) within limits from l = 0 to l = 2πr
Hence, B = (μ0/4π) (i/r2 2πr∫ dl = μ0i/2r
Through n turns of the coil of radius r, instead of one turn of ampere torrent flow, if n times more current flows, then there will be n times more magnetic induction or magnetic field. So in that type of magnetic induction,
B = [μ0ni/2r] Wb.m^-2
The Biot Savart Law can also be applied in the following ways:
- Magnetism can be calculated by the law even on the level of molecules or atoms.
- In aerodynamics, vortex lines can be used to determine the velocity of an air stream.
Conclusion
This law states that each factor influencing the field influences the magnetic field at a specific point in space from one short segment of a current-carrying conductor. On top of that, the magnetic field at a point is influenced by how far the point is from the conductor.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





