Electromagnetism is a physics branch that deals with the study of electromagnetic forces. It is a type of interaction that occurs between particles that are electrically charged in nature. Electromagnetic fields are composed of electric fields and magnetic fields, and together they produce what is known as electromagnetic force, and the connection between both fields is known as Biot- Savart Law.
Jean-Baptiste Biot and Felix Savart were the first scientists to come up with a theory that there is a relationship between electric fields and magnetic fields. Together in 1820, they came up with an equation that proved that a magnetic field is generated in the presence of electric current. The Biot-Savart Law forms the basis of magnetostatics and is Coulomb’s law equivalent in magnetostatics. Let’s have a look and understand more about the Biot-Savart Law and its applications.
What is the Biot-Savart Law?
An electric current that is flowing in a conductor or any moving electric charge is set to produce a magnetic field. The amount of magnetic field built at any point in the nearby space is considered the sum of all the influences from each small current-carrying conductor nearby. The law states that the magnetic field at any point in space is directly from a current-carrying conductor, depending on a lot of factors that can influence the field. The factors are:
Firstly, the value of the magnetic field at any point is directly proportional to two things – the value of current in the conductor and the length of the current-carrying segment.
Secondly, the value of the field also depends on the position of the point concerning the segment of the current. The field is set to be the greatest if the line from the point to the shortest segment of current is at a right angle to the current segment. The magnetic field starts to reduce if the angle gets smaller and eventually becomes zero when the point lies on the line of which the current element is a part.
Lastly, the magnetic field is impacted by the distance between the point and the current element. It has been established that if the distance is x between them then the field is x2 smaller. In simple words, the value of a magnetic field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of the magnetic field.

Application of the Biot- Savart Law
There are several applications of the Biot-Savart Law, some of them being:
The force between two parallel and long current-carrying conductors:
We can establish a relationship that two long and parallel current-carrying wires will attract each other if the current is in the same direction and repel each other if the current is in the opposite direction.
Consider two parallel wires A and B, at a distance d, carrying current in a similar and opposite direction. Where the current is traveling in the same direction, wire A produces a field B1 at all nearby points. The magnitude of B1 due to current I1 at a distance of d would be
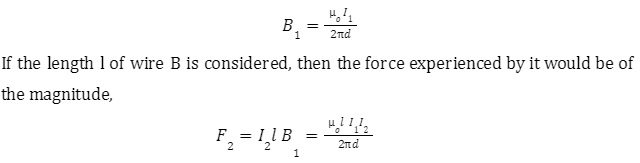
Direction F2 can be evaluated using the vector rule. It lies in the plane while pointing to the left.
The direction of force is towards A if I2 is in the same direction as I1 and is away from A if it’s in the opposite direction.
Force per unit length of wire B is

If ‘i’ is the current flowing through one turn of wire radius of ‘r’, magnetic induction at the center of the coil would be calculated due to the flow of current through the coil.
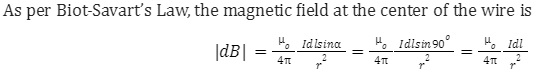
In this case, as the tangent at the midpoint and radius drawn at the point at a perpendicular. As a result of this, the magnetic induction due to the circular wire would be equal to the sum of magnetic induction produced. This is because all the magnetic induction would flow in the same direction. So, the total magnetic induction due to the current flowing in the whole wire is obtained by integrating the above equation within limits from l = 0 to l = 2πr
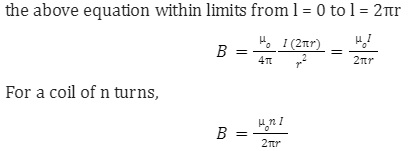
Importance of the Biot-Savart Law
The law is very relevant when it comes to small conductors carrying current.
The law applies to the symmetrical current distribution.
The law is very similar to Coulomb’s law in electrostatics.
Conclusion
So what we have discussed today is the Biot-Savart Law and why the law is significantly important in the field of electromagnetism. After reviewing the application of the Biot-Savart Law, one can easily understand the basic concept of the rule. The key finding is that current flowing through a conductor or any moving particle that is electronically charged will produce the magnetic field. The amount of magnetic field generated depends on several factors, which form the formula of the Biot-Savart Law.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






