As you know, the nucleus plays a very vital role in every field of science whether it is in physics or in chemistry or in biology. Here we explore the theory of nucleus and its binding energy per nucleon. In physics, it is a very important topic and pretty much interesting too. Have you ever wondered when you think about the nucleus of an atom? Has your brain ever raised questions such as where the nucleus is present? What does it actually look like? What’s its role? Here, we shall look for the answers for these questions. But before getting into our topic, let’s understand the basic properties and definition of nucleus and atoms.
What is nuclear binding energy?
The energy which is required to break the carbon atom into smaller nuclei by breaking the nuclear force is called nuclear binding energy.
Definition – To split the nucleus of an atom into smaller or lighter nuclei or into its nucleons forming an individual mass of proton and neutron, some amount of energy is required and that energy is called nuclear binding energy.
You should know,
The total of the masses of protons and neutrons is always less than the mass of nuclei.
BINDING ENERGY PER NUCLEONS
The difference between nuclear attraction and disruptive energy is the binding energy per nucleon. For calculating the binding energy per nucleon, we have to convert mass to energy by using formula which is given by Einstein.
E = mc2
Where, E is the binding energy of nucleus
c is the speed of light in vacuum
m is the mass difference
This formula is called binding energy per nucleon formula.
NOTE – Mass must be taken in kg.
VARIATION OF BINDING ENERGY WITH MASS NUMBER
The binding energy is constant for atomic numbers but it varies with atomic masses of elements. Also the binding energy is less for both light and heavy nuclei.
By this we understands that,
1) To produce binding energy per nucleon the force should be attractive and sufficiently strong.
2) The binding energy is less for heavy and light nuclei because of the fact that their nucleus is of short range.
3) If the nucleus is at a distance more than the nuclear force from the particular nucleons then it will not show any kind of influence on binding energy.
4) Nucleons having a maximum range of nuclear force then its binding energy will be proportional to that.
VARIATION OF BINDING ENERGY WITH MASS NUMBER
Let’s understand the variation of binding energy with mass number.
To understand the variation of binding energy with mass number, we need to draw a graph between these two parameters. By this, we understand that,
- To produce binding energy per nucleon, the force should be attractive and sufficiently strong.
- The binding energy is less for heavy and light nuclei because their nucleus is short-range.
- If the nucleus is at a distance more than the nuclear force from the particular nucleons, it will not influence binding energy.
- Nucleons having a maximum range of nuclear force, their binding energy will be proportional.
Let’s take an example to understand this concept in a better way,
Note – The fused heavier nuclei have more binding energy when compared to the lighter nuclei. This means that the final nucleus is more tightly bound than the initial one.
In simple words, when mass increases, the binding energy per nucleon decreases.
STABILITY OF ELEMENTS BASED ON THE BINDING ENERGY PER NUCLEONS
There are two major factors that determine nuclear stability.The neutron/proton ratio is one, while the total number of nucleons in the nucleus is the other.
Those elements who have greater mass defect and have higher binding energy are considered to be more stable.
As a result, nuclear stability is proportional to nuclear binding energy.
Example- Iron – 56 has more binding energy value thus the nucleus of iron is most efficiently bounded and is most stable.
MASS DEFECT
Mass Defect
given equation describes the relationship between energy and mass:
E = mc2
The speed of light is denoted by c. The binding energy of nuclei is so great that they can hold a lot of mass.
Because energy is released when the nucleus is produced, the actual mass is always smaller than the sum of the atomic masses of the nucleons. This energy is made up of mass, called mass defect since it is exerted from the overall mass of the initial atom. This mass is absent from the final proton and neutron, the energy released during nuclear reactions.
𝚫M = (Zmp + Nmn) – MA
M – mass defect
MA – the mass of the nucleus
mp – mass of a proton (1.00728 amu)
mn – the mass of a neutron (1.00867 amu)
Z – number of protons
N – number of neutrons
Binding Energy Calculation
Binding energy calculation can be done in the following way:
Binding Energy = mass defect x c2
where c = speed of light in vacuum
c = 2.9979 x 108 m/s.
Binding Energy is expressed in terms MeV’s/nucleon or kJ/mole of nuclei.
Conclusion
From all of the above we come to the conclusion. We learned that binding energy is the energy which is required to split the heavier nucleus of an atom into a smaller one by forming the mass of their individual proton and neutron. As we studied above, higher the number of nucleons, higher will be the binding energy. Stability of atoms is also defined by this energy. The atom will be more stable if the binding energy is higher. The energy from the fusion and fission used to generate electric power in several industries. By the Einstein formula that is E = mc2, we can determine the nuclear binding energy.
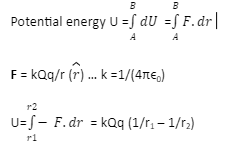
- What is the meaning of a reference point?
The point at which the electric potential can be considered as equal to zero is called the reference point. For a system of two charges when the second charge q in the electric field of Q, is displaced from point A at r1 to point B at r2; potential energy of the system of two charges is given by, U= kQq (1/r2 – 1/r1)
If we consider the initial distance r1= as the reference point then we get potential energy U = kQq (1/r2).
- What are the units of Electric Potential energy?
The SI unit of Electric potential energy is the same as that of energy, which is Joule (J).
Another unit of measurement is electron Volt (eV).
1ev = 1.6 x 10-19 joule.
- What is the meaning of Electric Potential or what is the difference between electric potential and electric potential energy?
Electric potential energy is defined as the amount of work done to displace a charge from one point to another point against the electrostatic force field.
Electric potential can be defined in terms of electric potential energy as equivalent to the work done to displace unit positive charge from one point to another point against the electrostatic field. Thus, electric potential is equal to electric potential energy per unit charge.
Therefore, Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
This expression gives the relation between electric potential and electric potential energy.
- What is the SI unit of Electric Potential?
Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
SI unit of Electric Potential energy (U) is joule (J), charge (q) = Coulomb (C)
Thus, the SI unit of Electric Potential is Joule/C or Volt.
- How is potential energy calculated for a system of N charges?
For a charge q brought from infinity (point of reference) to a point (at position r) in presence of another charge q1 the potential energy is given as U1 = kq1q/r. In case of a system of charge, work done or potential energy obeys the principle of superposition. Hence the total potential energy is given as the sum of potential energy between the charges present in the system.
- Why is the Electrostatic potential energy path independent?
Electrostatic field is a conservative field. That is electrostatic force law obeys inverse square law, thus the electrostatic force is a conservative force. Potential energy in consideration with the electrostatic field is defined as the work done against the electrostatic force. That is U =F.dr. Since the force field is conservative work done/ potential energy over a closed path is zero. This implies that electrostatic potential energy / work done is path independent. It depends on the initial and final position only.
- What is the expression for electrostatic potential due to a point charge?
Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
For a unit positive charge, V = U = kQ/r. This is the expression for Electric potential due to a point charge Q at a distance r from the charge.
Conclusion
Electrostatic potential energy is considered in respect to the Electrostatic field. Word done is stored as potential energy. When this work is done to displace a charged particle in the presence of an electric field, it is stored as electrostatic potential energy.
The SI unit of electric potential energy is joule.
The electric potential is defined in terms of electrostatic potential energy. Electric potential is defined as electric potential energy per unit charge i.e. work done to displace unit charge. SI unit of electric potential is joule/C.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






