The x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis are three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes that make up the three-dimensional coordinate system.
We may find the point using the ordered pair (x,y) in the rectangular coordinate system, where x indicates the point’s horizontal position and y represents its vertical position. We name this system the two-dimensional coordinate system because it only requires two directions to find a point on a plane.
Now, we’ll need three integers to pinpoint the location in space: (x,y,z). The ordered triple is what it’s called. This is how the origin of the 3D coordinate system was discovered. We now have three coordinate axes that are mutually perpendicular to each other, rather than two. The x and y axes are the two horizontal axes that are perpendicular to each other in 3D coordinate systems. The z-axis becomes the only vertical axis in three dimensions.
Coordinate System
Rectangular (or Cartesian), cylindrical, and spherical coordinate systems are the three most popular in applied mechanics. The purpose of this section is to define these coordinate systems and to develop the equations for the transformation of each coordinate system’s vector components with regard to the others.
Rectangular (or Cartesian) Coordinate System
The xy-plane or ‘coordinate plane’ is another name for the rectangular coordinate system.
The x-axis is the horizontal number line. The y-axis refers to the vertical number line. The rectangular coordinate system is made up of the x- and y-axes. A plane is divided into four quadrants by these axes. Roman numerals are used to identify the quadrants, which start at the upper right and move counter clockwise. See (Figure).
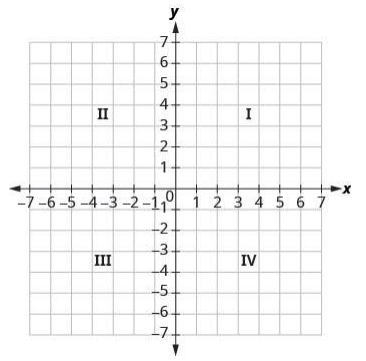
The word ‘quadrant’ comes from the word ‘quad,’ which meaning ‘four.’
Distance between Two Points in 3D
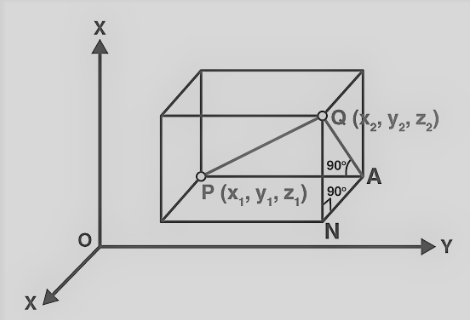
A system of rectangular axes OX, OY, and OZ is represented by two points P(x1,y1,z1) and Q(x2,y2,z2).
When planes parallel to the coordinate plane are drawn from the points P and Q. Then, with PQ as the diagonal, we have a rectangular parallelepiped.
A right angle is being formed by PAQ. It allows us to use the Pythagoras theorem in ∠PAQ triangles.
Therefore, now you get PQ2=PA2+AQ2…(1)
Also note that, in triangle ANQ, ∠ANQ is a right angle. Now, we need to apply the Pythagoras theorem to ΔANQ as well.
Now, we obtain AQ2=AN2+NQ2…(2)
From equation (1) and equation (2), we get PQ2=PA2+NQ2+AN2.As we know the coordinates of the points P and Q, PA = (y2−y1), AN = (x2−x1) and NQ = (z2−z1).
Hence, PQ2 = (x2−x1)2 + (y2−y1)2 + (z2−z1)2
Finally, the formula to obtain the distance between two points in 3D is –
PQ2 = (x2−x1)2 + (y2−y1)2 + (z2−z1)2
That formula can give you the distance between two points P(x1,y1,z1) and Q(x2,y2,z2) in 3D.
Also note that the distance of any point Q (x, y, z) in space from origin O (0, 0, 0), can get expressed as, OQ = x2 + y2 + z2
Conclusion
A Cartesian coordinate system on a plane uniquely identifies each point by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances between two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line in the system is referred to as a coordinate axis or simply axis (plural axes), and the location where they intersect is known as the system’s origin (0, 0). The signed distances from the origin of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes can alternatively be defined as coordinates.
The distance between two points is Formula in three dimensions
The distance between two points P(x1, y1, z1) and Q(x2, y2, z2) = PQ = √ [ (x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2 + (z2 – z1)2]
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






