A hyperbola is the set of all points in a plane where the difference of those points from two fixed points (also known as foci) in the plane is a constant.
Such that |P1F1-P1F2| =| P2F1- P2F2 |=| P3F1 – P3F2|= constant.
Hyperbola can also be defined as a section formed when a plane intersects a double right angle circular cone at an angle such that both portions of the cones are mirror images of each other. The result of the section resembles two infinite bows.
This intersection creates two separate, borderless curves that are mirror images of each other.
Terms Used in Hyperbola
Foci: It is a plural of focus and are the two points on a hyperbola.
Vertices: These are the points where the intersection with the transverse axis happens on a hyperbola.
Transverse axis: Major axis of a hyperbola, and a line passes through the focus.
Conjugate axis: A line passes through the centre and perpendicular to the transverse axis.
Centre: The intersection point of the transverse and conjugate axis.
Equilateral Hyperbola: When a = b in a hyperbola.
Basic Property of Hyperbola
Some of the basic properties of the hyperbola are as follows:
Hyperbola has two axes of symmetry, i.e. both the x-axis and y-axis.

- If the lengths of the conjugate and transverse axes are similar, then a hyperbola is equilateral or rectangular.
- Asymptotes of the hyperbola are where two lines intersect at the centre of a hyperbola.
- The line perpendicular to the transverse axis and passing through any of the foci, which are parallel to the conjugate axis, is the latus rectum of the hyperbola.
Types of Hyperbola
There are two types of hyperbola: Horizontal Hyperbola and Vertical Hyperbola.
- Horizontal Hyperbola: In this type of hyperbola, the conjugate’s axis is the x-axis, and the standard formula with the centre (0, 0) is:

Where,
- the coordinates of the vertices = (a, 0)
- the coordinates of the co-vertices = (0, b)
- the coordinates of the foci = (c, 0)
- the length of the transverse axis = 2a
- the length of the conjugate axis = 2b
- the distance between the foci = 2c, where, c2= a2 + b2
- the equations of the asymptotes = y = bax
2. Vertical Hyperbola: In this type of hyperbola, the conjugate’s axis is the y-axis, and the standard formula with the centre (0, 0) is:

Where,
- the coordinates of the vertices = (0, a)
- the coordinates of the co-vertices = (b, 0)
- the coordinates of the foci = (0, c)
- the length of the transverse axis = 2a
- the length of the conjugate axis = 2b

Problems on Hyperbola
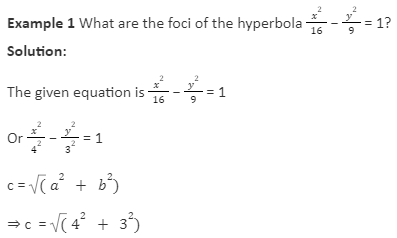
c= ( 16 + 9)
=25
= 5
The foci of hyperbola (± c , 0)
(± 5 , 0)
Example 2: For the given equation below, find the coordinates of the vertices, the foci, the eccentricity, and the length of the latus rectum of the hyperbolas:

Example 3: Find the equation of the hyperbola with foci (0, ± 5) and vertices (0, ± 3 ).

1
Since vertices are (0, ± 3 ), a = 3
Also, since foci are (0, ± 5); c = 5
c = ( a2 + b2)
5 = ( 32 + b2)
Squaring both sides
52 = 32 + b2
25 = 9 + b2
b2 = 25 – 9
b2 = 16
b = 16
b = 4

Conclusion
In the above article, we have defined the basics of Hyperbola along with its properties, types and so on. Hyperbola is an open curve formed by the intersection of a circular cone with a plane at a smaller angle in a symmetrical manner. It has two axes of symmetry. Besides, there are two types of Hyperbola – Horizontal Hyperbola and Vertical Hyperbola.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






