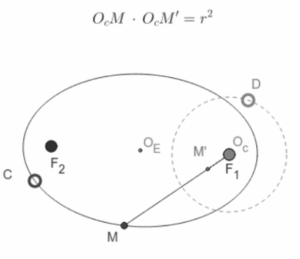
Given is an ellipse with foci points F1 and F2 and a single point C. Inversion is performed with respect to a circle having a centre Oc and radius r. On the circle, point D is a point. By dragging, D we can modify the radius r. A random point on the ellipse is called a point M. With respect to the above circle, point M’ is the image of M under inversion (OcM.OcM’ = r²).
M¹ will draw the locus of the inverse of the ellipse as M moves along the ellipse.
The inverse of the ellipse is a Limaçon with no loop (a dimpled Limaçon) if the circle’s centre is in one of the foci.
- Change the ellipse or move the point C or F2 to watch how the Limaçon changes.
- Change the radius of the circle by dragging point D and watch how it impacts Limaçon.
- Continue experimenting by dragging the circle’s centre Oc to other locations.
Ellipse
The ellipse is one among the conic sections that are produced when a plane cuts the cone at an angle with the bottom. If the cone is intersected by the plane, parallel to the bottom, then it forms a circle.
An ellipse is defined as the set of all points where the sum of the distances from two fixed points is constant. In other words, we can say that there are two fixed points, called foci. If we trace out all points where the distance between the primary focus and a point plus the distance between the secondary focus and the same point remains constant, we can draw an ellipse.
Ellipse with center of inversion at a vertex
An ellipse’s general equation is
x² / a² + y² / b² = 1
When you translate it such that the origin to one of the vertices, you get
(x-a)² / a² + y² / b² = 1
Upon rearranging we get,
( x² / 2a )+ ( ay² / 2b² ) = x
Let, c = 1/2a and d = (a / 2b² ), then we get,
cx² + dy² = x
By setting c = 0 and d = 1, the parabola above now fits into this framework. The inverse equation is as follows:
cx² / ( x²+y² )² + dy² / ( x²+y² )² = x / ( x²+y² )
It can also be written as
x ( x² + y² ) = cx² + dy²
The conchoids of de Sluze are a family of curves described by this equation. In addition to the Diocles cissoid, this family also includes the Maclaurin trisectrix (d = – c / 3 ) and the right strophoid (d = – c).
Ellipse with the centre of inversion at a centre
Inverting an ellipse or hyperbola’s equation cx² + dy²= 1 results in
( x² + y² ) = cx² + dy²
The hippopede, to be precise. This is the lemniscate of Bernoulli for d = – c.
Ellipse with the arbitrary centre of inversion
The inverse of a conic (other than a circle) is a circular cubic if the centre of inversion is on the curve, and a bicircular quartic otherwise, according to the degree formula. Inverse curves are logical because conics are rational. Any rational circular cubic or rational bicircular quartic, on the other hand, is the inverse of a conic. In fact, any such curve must have a real singularity and the inverse curve will be a conic by the degree formula if this point is used as the centre of inversion.
Anallagmatic Curve
A curve that inverts into itself is called an anallagmatic curve. The circle, cardioid, oval of Cassini, strophoid, and trisectrix of Maclaurin are examples.
Conclusion
Inversive geometry is the study of inversion, a Euclidean plane transformation that maps circles or lines to other circles or lines while maintaining the angles between crossing curves. When you apply an inversion to a challenging geometry issue, it becomes considerably easier to solve. Higher-dimensional spaces can benefit from the concept of inversion.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




