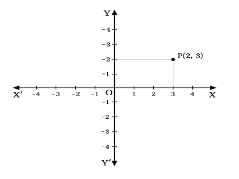Two-dimensional space, sometimes referred to as 2D space, 2-space, or bi-dimensional space, is a geometric environment where an element’s location is determined by two values, or parameters (i.e., point). The most common illustration of a two-dimensional Euclidean space is the set of real number pairs with the required structure. See dimension for a generalisation of the idea. The physical cosmos may be thought of as being projected onto a plane in two-dimensional space. The two dimensions are known as length and breadth, and the space is typically conceived of as a Euclidean space.
Two Dimensional Space
Two-dimensional space, often referred to as two-dimensional space, two-dimensional space, or bi-dimensional space, is a geometric environment in which a point’s location on the plane depends on the values of two parameters. The standard example of a Euclidean plane, or two-dimensional Euclidean space, is frequently a collection of pairs of real numbers (real coordinate space) with the necessary structure; for an extension of the notion, see dimension. The physical cosmos may be thought of as being projected onto a plane in two-dimensional space. The two dimensions are known as length and breadth, and the space is typically conceived of as a Euclidean space.
Types of Two Dimensional Space
According to their curvature, the kinds of a two-dimensional space can be arranged. Parallel lines often come together when there is positive curvature, and they diverge when there is negative curvature.
Spherical
Spherical planes have a positive curvature and may be conceptualised as a two-dimensional representation of a sphere on a ball’s surface. Walking along a straight path will ultimately bring an object in a spherical area back to its initial place, just as two parallel lines will eventually circle around the sphere and meet again.
Euclidean
The ordinary flat plane that abides by the postulates of Euclidean geometry is known as the Euclidean plane, which has a zero curvature.
Hyperbolic
The curvature of the hyperbolic plane is negative. Two parallel lines will diverge as a result, earning them the moniker ultra parallel
Two Dimensional Space Example
The x-axis and the y-axis are the coordinate axes in this illustration. At point O, the two coordinate of the axes are perpendicularly divided.
Any point in the plane may be located using the point O, which is known as the origin of the two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.
The term “two-dime
Two Dimensional Shape
nsional form” (or “2D shape”) refers to a flat shape having just two dimensions—its length and width—and no thickness or depth. A sheet of paper is a two-dimensional object as an illustration. It has a length and a breadth, but neither a depth nor a height. Squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and hexagons are a few examples of typical 2D forms. A 3D (three-dimensional) form, in contrast, has three dimensions: length, breadth, and height. A dice, for instance, has three dimensions since it has three different dimensions: length, breadth, and height. Cuboids, cones, pyramids, and cylinders are a few examples of typical 3D forms.
Types of 2d Shapes
Based on the length and internal angles, a 2D form can be categorised as regular or irregular:
If all of a two-dimensional form’s (2D shape) sides are the same length and all of its interior angles have the same measurement, the shape is said to be regular.
If all of a two-dimensional object’s sides and angles have different lengths, the shape is said to be irregular.
Example
A few examples of 2D shapes are the circle, triangle, rectangle, pentagon, and square. With the exception of the circles, we may argue that all 2D forms are polygons. While circles have a curved form, polygons have a closed structure with sides.
A triangle is a three-sided, triangular-shaped object in space. A form with four sides and four corners is called a rectangle. They could observe that the lengths of the opposing sides are equal.
All four sides of a square, which is a planar form, are the same length. This kind of object is oblong.
A circle is a spherical form without edges or corners.
Conclusion
In Euclidean geometry, the entire space is divided into four equal sections by the intersecting two perpendicular number-lines at their midpoint. Every point in two perpendicular directions is measured from their bisection point using the number lines on the perpendicular lines as a base line.
The Cartesian system known as the two-dimensional space is used in this geometric environment to assist us determine the precise location of each point using two numerical values in the plane.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out