A straight line is any line that can be traced by a point moving in a direction with zero curvature. A straight line has only one dimension and length and stretches in two directions indefinitely. It is a crucial geometric notion that can be applied in a variety of ways.
The slope of a line:
The slope or gradient of line I is called tanθ if θ is its inclination. The slope of a line with an inclination of less than 90°. The letter ’m’ stands for it.
Therefore, m = tanθ, θ ≠ 90°
The slope of the x-axis is presumed to be zero when the slope of the y-axis is unknown.
The angle between two lines:
Consider the two non-vertical lines L₁ and L₂ with slopes m₁ and m₂, respectively, where α₁ and α₂ are the respective inclinations of lines L₁ and L₂. The slope of the lines m₁ and m₂ is then calculated as
m1 = tanα₁ and m2 = tanα₂
When two lines intersect, they form two pairs of vertically opposing angles, with the total of any two adjacent angles being 180 degrees from the property. Assume that θ and φ are the intersecting angles of the lines L₁ and L₂. Then
Θ = α₂ – α₁, and α₁, α₂ ≠ 90°
As a result,
Tanθ = tan(α₂-α₁) = (tanα₂-tanα₁)/(1+tanα₁tanα₂)
Tanθ = (m₂-m₁)/(1+m₁m₂)
Since 1+m₁m₂ ≠ 0 and φ = 180° – θ so,
Tan φ = tan(180°-θ) = -tanθ = -(m₂-m₁)/(1+m1m2)
Case 1: If (m₂-m₁)/(1+m₁m₂) is positive, then tanθ will be positive and tanφ negative, indicating that θ will be acute and φ obtuse, respectively.
Case 2: If (m₂-m₁)/(1+m₁m₂) is negative, then tanθ will be negative and tanφ will be positive, respectively, indicating that θ will be obtuse and φ acute.
As a result, the acute angle formed by the lines L₁ and L₂ with slopes m₁ and m₂ is given by
Where, 1 + m₁m₂ ≠ 0 tanθ = |(m₂-m₁)/(1+m₁m₂)|
The obtuse angle can then be calculated using φ =180° – θ.
Various forms of equations of a line:
The following are the many forms of the equation of the line that is presented in straight line class 11.
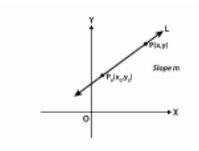
Slope-point form:
Assume P₀(x₀, y₀) is a fixed point on a non-vertical line L with m as its slope. If P (x, y) is an arbitrary point on L, then the point (x, y) lies on the line with slope m through the fixed point (x₀, y₀) if and only if the coordinates of the object satisfy the equation below.
y – y₀ = m (x – x₀)
Two-point form:
Let’s look at the line. L travels between two places. P₁(x₁, y₁) and P₂(x₂, y₂) are general points on L, while P (x, y) is a general point on L.
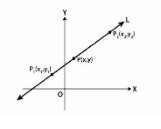
y – y₁/x – x₁ = y₂ – y₁/x₂ – x₁
y – y₁ = (y₂ – y₁)(x – x₁)/(x₂ – x₁)
As a result, the equation of the line going through the points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) is
y – y₁ = (y₂ – y₁)(x – x₁)/(x₂ – x₁)
Slope-intercept form:
Assume a line L with slope m intersects the y-axis at a distance c from the origin, and the distance c is called line L’s y-intercept.
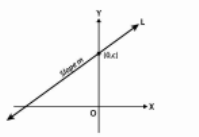
y – c = ( x – 0 )
As a result, if and only if, the point (x, y) on the line with slope m and y-intercept c lies on the line.
y = m x +c
The value of c will be positive or negative depending on whether the intercept is generated on the positive or negative side of the y-axis.
Intercept form:
Consider the intersection of the axes at x-intercept and y-intercept b by a line L. L contacts the x-axis at (a, 0) and the y-axis at (b, 0).
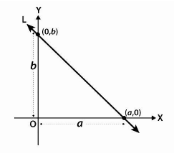
x/a + y/b = 1
As a result, it becomes
y – 0 = (b – 0)(x – a)/(0 – a)
As a result, the equation of the line with the intercepts a and b on the x- and y-axis, respectively, is x/a + y/b = 1
Conclusion:
A straight-line graph is used in medicine and pharmacy to identify the precise strength of drugs. In the study process and the production of the government budget, straight-line graphs are used. In chemistry and biology, straight-line graphs are utilized. Straight-line graphs are used to determine whether our body weight is healthy for our height.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out